Mammalian capping enzyme binds RNA and uses protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism
- PMID: 9770468
- PMCID: PMC22813
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12226
Mammalian capping enzyme binds RNA and uses protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism
Abstract
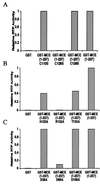
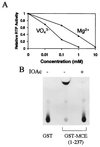
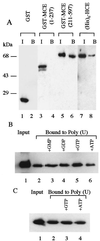
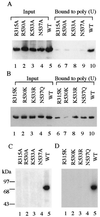
Mammalian capping enzymes are bifunctional proteins with both RNA 5'-triphosphatase and guanylyltransferase activities. The N-terminal 237-aa triphosphatase domain contains (I/V)HCXXGXXR(S/T)G, a sequence corresponding to the conserved active-site motif in protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs). Analysis of point mutants of mouse RNA 5'-triphosphatase identified the motif Cys and Arg residues and an upstream Asp as required for activity. Like PTPs, this enzyme was inhibited by iodoacetate and VO43- and independent of Mg2+, providing additional evidence for phosphate removal from RNA 5' ends by a PTP-like mechanism. The full-length, 597-aa mouse capping enzyme and the C-terminal guanylyltransferase fragment (residues 211-597), unlike the triphosphatase domain, bound poly (U) and were nuclear in transfected cells. RNA binding was increased by GTP, and a guanylylation-defective, active-site mutant was not affected. Ala substitution at positions required for the formation of the enzyme-GMP capping intermediate (R315, R530, K533, or N537) also eliminated poly (U) binding, while proteins with conservative substitutions at these sites retained binding but not guanylyltransferase activity. These results demonstrate that the guanylyltransferase domain of mammalian capping enzyme specifies nuclear localization and RNA binding. Association of capping enzyme with nascent transcripts may act in synergy with RNA polymerase II binding to ensure 5' cap formation.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

