A DNA damage and stress inducible G protein-coupled receptor blocks cells in G2/M
- PMID: 9770487
- PMCID: PMC22832
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12334
A DNA damage and stress inducible G protein-coupled receptor blocks cells in G2/M
Abstract
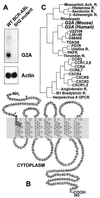
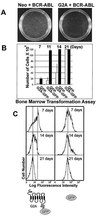
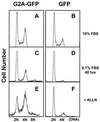
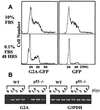
Cell cycle progression is monitored by highly coordinated checkpoint machinery, which is activated to induce cell cycle arrest until defects like DNA damage are corrected. We have isolated an anti-proliferative cell cycle regulator named G2A (for G2 accumulation), which is predominantly expressed in immature T and B lymphocyte progenitors and is a member of the seven membrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptor family. G2A overexpression attenuates the transformation potential of BCR-ABL and other oncogenes, and leads to accumulation of cells at G2/M independently of p53 and c-Abl. G2A can be induced in lymphocytes and to a lesser extent in nonlymphocyte cell lines or tissues by multiple stimuli including different classes of DNA-damaging agents and serves as a response to damage and cellular stimulation which functions to slow cell cycle progression.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

