Riboregulation in Escherichia coli: DsrA RNA acts by RNA:RNA interactions at multiple loci
- PMID: 9770507
- PMCID: PMC22852
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12456
Riboregulation in Escherichia coli: DsrA RNA acts by RNA:RNA interactions at multiple loci
Abstract
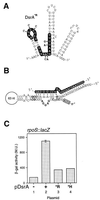
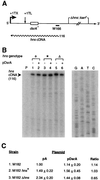
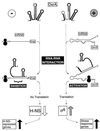
DsrA is an 87-nt untranslated RNA that regulates both the global transcriptional silencer and nucleoid protein H-NS and the stationary phase and stress response sigma factor RpoS (sigmas). We demonstrate that DsrA acts via specific RNA:RNA base pairing interactions at the hns locus to antagonize H-NS translation. We also give evidence that supports a role for RNA:RNA interactions at the rpoS locus to enhance RpoS translation. Negative regulation of hns by DsrA is achieved by the RNA:RNA interaction blocking translation of hns RNA. In contrast, results suggest that positive regulation of rpoS by DsrA occurs by formation of an RNA structure that activates a cis-acting translational operator. Sequences within DsrA complementary to three additional genes, argR, ilvIH, and rbsD, suggest that DsrA is a riboregulator of gene expression that acts coordinately via RNA:RNA interactions at multiple loci.
Figures
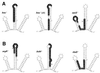

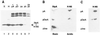
References
-
- Rastinejad F, Conboy M J, Rando T A, Blau H M. Cell. 1993;75:1107–1117. - PubMed
-
- Simons R W, Kleckner N. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:567–600. - PubMed
-
- Delihas N. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:411–414. - PubMed
-
- Henkin T M. Annu Rev Genet. 1996;30:35–57. - PubMed
-
- Moss E G, Lee R C, Ambros V. Cell. 1997;88:637–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

