Chlorophyll a oxygenase (CAO) is involved in chlorophyll b formation from chlorophyll a
- PMID: 9770552
- PMCID: PMC22897
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12719
Chlorophyll a oxygenase (CAO) is involved in chlorophyll b formation from chlorophyll a
Abstract
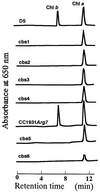
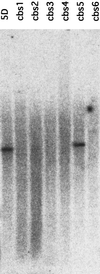
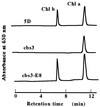
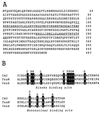
Chlorophyll b is an ubiquitous accessory pigment in land plants, green algae, and prochlorophytes. Its biosynthesis plays a key role in the adaptation to various light environments. We isolated six chlorophyll b-less mutants by insertional mutagenesis by using the nitrate reductase or argininosuccinate lyase genes as tags and examined the rearrangement of mutant genomes. We found that an overlapping region of a nuclear genome was deleted in all mutants and that this encodes a protein whose sequence is similar to those of methyl monooxygenases. This coding sequence also contains putative binding domains for a [2Fe-2S] Rieske center and for a mononuclear iron. The results demonstrate that a chlorophyll a oxygenase is involved in chlorophyll b formation. The reaction mechanism of chlorophyll b formation is discussed.
Figures

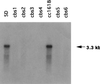
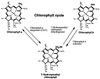
References
-
- Anderson J M. Annu Rev Plant Physiol. 1986;37:93–136.
-
- Björkman O, Boardman N K, Anderson J M, Thorne S W, Goodchild D J, Pyliotis N A. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb. 1972;71:115–135.
-
- Palenik B, Haselkorn R. Nature (London) 1992;355:265–267. - PubMed
-
- Urbach E, Robertson D L, Chisholm S W. Nature (London) 1992;355:267–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

