Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset
- PMID: 9771209
- PMCID: PMC1752612
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.57.6.350
Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the role of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the wrist in detecting early joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: MRI was performed on 42 patients with early RA (median symptom duration of four months). Scans were scored separately by two musculoskeletal radiologists using a newly devised scoring system, which was validated. MRI findings were compared with plain radiography, clinical measures, and HLA-DRB*01/04 genotyping.
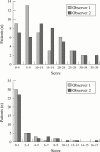
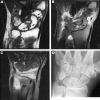
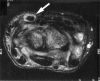
Results: Interobserver reliability for the overall MRI score was high (r = 0.81) as was intraobserver reliability (r = 0.94 for observer 1 and 0.81 for observer 2). There was more variation in scoring synovitis (interobserver reliability: r = 0.74). Erosions were detected in 45% of scans (19 of 42), compared with 15% of plain radiographs. The most common site for erosions was the capitate (39%), for synovitis the ulnar aspect of the radiocarpal joint, and for tendonitis, the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon. The total MRI score and MRI synovitis score correlated most significantly with C reactive protein (r = 0.40 and 0.42 respectively, p < 0.01). The MRI erosion score was highly correlated with MRI bone marrow oedema (r = 0.83) as well as the Ritchie score and disease activity score (r = 0.32, p < 0.05). HLA-DRB1*04 or *01 (shared epitope +ve) was found in 76% of patients; 84% of those with MRI erosions and 69% of those without (NS, p = 0.3).
Conclusions: A high proportion of RA patients develop MRI erosions very early in their disease, when plain radiography is frequently normal. MRI of the dominant wrist may identify those requiring early aggressive treatment.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

