Enhanced fibroblast growth factor 5 expression in stromal and exocrine elements of the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis
- PMID: 9771418
- PMCID: PMC1727183
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.43.1.134
Enhanced fibroblast growth factor 5 expression in stromal and exocrine elements of the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis
Abstract
Background: Fibroblast growth factor 5 (FGF-5) belongs to a group of mitogenic and angiogenic heparin binding growth factors but its potential role in chronic inflammatory conditions is not known.
Aims: To compare FGF-5 expression in the normal pancreas and in the pancreas of patients with chronic pancreatitis (CP) and to characterise FGF-5 expression and secretion in TAKA-1 cells, an immortalised Syrian hamster pancreatic duct cell line.
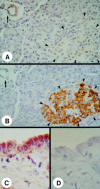
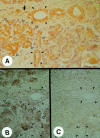
Methods and results: Northern blotting revealed the presence of a 4.0 kb FGF-5 mRNA transcript in both normal and CP tissue samples. Densitometric analysis indicated that the transcript levels were increased by a factor of 1.44 in CP tissue samples compared with normal tissue samples (p = 0.039). By immunohistochemisty and in situ hybridisation, FGF-5 was faintly expressed in ductal and islet cells in the normal pancreas. In contrast, in CP tissue samples, there was abundant expression of FGF-5 in ductal, acinar, and islet cells, as well as in periductal fibroblasts. FGF-5 was also expressed in TAKA-1 cells as determined by Northern blotting. By immunoblotting of heparinsepharose precipitates, TAKA-1 cells were shown to secrete FGF-5 into the medium.
Conclusion: Exocrine and stromal derived FGF-5 has the potential to participate in autocrine and paracrine pathways that may contribute to the pathobiology of chronic pancreatitis.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
