Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification, a new method for analysis of spliced and unspliced Epstein-Barr virus latent transcripts, and its comparison with reverse transcriptase PCR
- PMID: 9774558
- PMCID: PMC105294
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.11.3164-3169.1998
Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification, a new method for analysis of spliced and unspliced Epstein-Barr virus latent transcripts, and its comparison with reverse transcriptase PCR
Erratum in
- J Clin Microbiol 1999 Nov;37(11):3788
Abstract
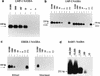
Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) assays were developed for direct detection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transcripts encoding EBV nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1), latent membrane proteins (LMP) 1 and 2, and BamHIA rightward frame 1 (BARF1) and for the noncoding EBV early RNA 1 (EBER1). The sensitivities of all NASBAs were at least 100 copies of specific in vitro-generated RNA. Furthermore, 1 EBV-positive JY cell in a background of 50,000 EBV-negative Ramos cells (the relative sensitivity) was detected by using the EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 NASBA assays. The relative sensitivity of the EBER1 NASBA was 100 EBV-positive cells, which was probably related to the loss of small RNA molecules during the isolation. The BARF1 and LMP2 NASBAs were evaluated on clinical material. BARF1 expression was found in 6 of 7 nasopharyngeal carcinomas (NPC) but in 0 of 22 Hodgkin's disease (HD) cases, whereas LMP2 expression was found in 7 of 7 NPCs and in 17 of 22 HD cases. For detection of EBNA1 transcripts in HLs (n = 12) and T- and B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (n = 3 and n = 2, respectively), NASBA was compared with reverse transcriptase (RT) PCR. Two samples were positive only with NASBA, and two other samples were positive only with RT-PCR; for all other samples, the RT-PCR and NASBA results were in agreement. We conclude that NASBA is suitable for sensitive and specific detection of the above-mentioned EBV transcripts, regardless of their splicing patterns and the presence of EBV DNA. The EBNA1, LMP2, and BARF1 NASBAs developed in this study proved to be reliable assays for detection of the corresponding transcripts in EBV-positive clinical material.
Figures

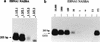

Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts.J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2689-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.5.2689-2697.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1313894 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: nasopharyngeal brushings reveal high Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and carcinoma-specific viral BARF1 mRNA.Int J Cancer. 2006 Aug 1;119(3):608-14. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21914. Int J Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16572427
-
Expression of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transcripts encoding homologues to important human proteins in diverse EBV associated diseases.Mol Pathol. 1999 Apr;52(2):97-103. doi: 10.1136/mp.52.2.97. Mol Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10474689 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular pathological studies on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infected cells and EBV-associated tumor cells].Nihon Rinsho. 1997 Feb;55(2):452-60. Nihon Rinsho. 1997. PMID: 9046840 Review. Japanese.
-
Co-Expression of the Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Latent Membrane Proteins and the Pathogenesis of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Aug 24;10(9):285. doi: 10.3390/cancers10090285. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30149502 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LINCATRA: Two-cycle method to amplify RNA for transcriptome analysis from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 12;10(12):e32896. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32896. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38988576 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Uses of Paper Microfluidics in Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;13(9):885. doi: 10.3390/bios13090885. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential expression of EBV proteins LMP1 and BHFR1 in EBV‑associated gastric and nasopharyngeal cancer tissues.Mol Med Rep. 2016 May;13(5):4151-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5087. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27052804 Free PMC article.
-
In nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 interacts with galectin 9 in membrane raft elements resistant to simvastatin.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(21):13326-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.21.13326-13337.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16227255 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the NucliSens Basic Kit assay for detection of Norwalk virus RNA in stool specimens.J Virol Methods. 2003 Mar;108(1):123-31. doi: 10.1016/s0166-0934(02)00286-0. J Virol Methods. 2003. PMID: 12565163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bijl J, van Oostveen J W, Kreike M, Rieger E, van der Raaij-Helmer L, Walboomers J M M, Corte G, Boncinelli E, van den Brule A J C, Meijer C J L M. Expression of HOXC4, -C5 and -C6 in human lymphoid cell lines, leukemias, and in benign and malignant lymphoid tissue. Blood. 1995;87:1737–1745. - PubMed
-
- Brink A A T P, Oudejans J J, Jiwa M, Walboomers J M M, Meijer C J L M, Vandenbrule A J C. Multiprimed cDNA synthesis followed by PCR is the most suitable method for Epstein-Barr virus transcript analysis in small lymphoma biopsies. Mol Cell Probes. 1997;11:39–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

