Development and evaluation of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on the 18-kilodalton matrix protein for diagnosis of primary EBV infection
- PMID: 9774594
- PMCID: PMC105330
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.11.3359-3361.1998
Development and evaluation of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on the 18-kilodalton matrix protein for diagnosis of primary EBV infection
Abstract
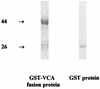
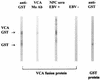
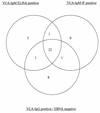
A new immunoglobulin M (IgM) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on the recombinant Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) matrix protein was developed. Compared to indirect immunofluorescence for the detection of IgM antibody to the EBV capsid antigen on clinical specimens, the sensitivity and specificity of the new IgM ELISA were 96 and 96%, respectively.
Figures
References
-
- Chan, K. H. Unpublished data.
-
- Evans A S, Niederman J C, Cenabre L C, West B, Richards V A. A prospective evaluation of heterophile and Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgM antibody tests in clinical and subclinical infectious mononucleosis: specificity and sensitivity of the tests and persistence of antibody. J Infect Dis. 1975;132:546–554. - PubMed
-
- Fleisher G, Lennette E T, Henle G, Henle W. Incidence of heterophile antibody responses in children with infectious mononucleosis. J Pediatr. 1979;94:723–728. - PubMed
-
- Gray J J, Wreghitt T G. Immunoglobulin G avidity in Epstein-Barr virus infections in organ transplant recipients. Serodiagn Immunother Infect Dis. 1989;3:389–393.
-
- Harnett G B, Palmer C A, Bucens M R. A modified immunofluorescence test for Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgM antibody. J Virol Methods. 1985;12:25–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

