Cak1 is required for Kin28 phosphorylation and activation in vivo
- PMID: 9774652
- PMCID: PMC109222
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.11.6365
Cak1 is required for Kin28 phosphorylation and activation in vivo
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol 2000 Mar;20(5):1898
Abstract
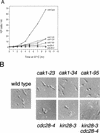
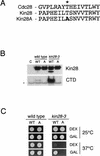
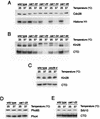
Complete activation of most cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) requires phosphorylation by the CDK-activating kinase (CAK). In the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the major CAK is a 44-kDa protein kinase known as Cak1. Cak1 is required for the phosphorylation and activation of Cdc28, a major CDK involved in cell cycle control. We addressed the possibility that Cak1 is also required for the activation of other yeast CDKs, such as Kin28, Pho85, and Srb10. We generated three new temperature-sensitive cak1 mutant strains, which arrested at the restrictive temperature with nonuniform budding morphology. All three cak1 mutants displayed significant synthetic interactions with loss-of-function mutations in CDC28 and KIN28. Loss of Cak1 function reduced the phosphorylation and activity of both Cdc28 and Kin28 but did not affect the activity of Pho85 or Srb10. In the presence of the Kin28 regulatory subunits Ccl1 and Tfb3, Kin28 was phosphorylated and activated when coexpressed with Cak1 in insect cells. We conclude that Cak1 is required for the activating phosphorylation of Kin28 as well as that of Cdc28.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase (CAK) in budding yeast unrelated to vertebrate CAK.Science. 1996 Sep 20;273(5282):1714-7. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5282.1714. Science. 1996. PMID: 8781234
-
CAK1 promotes meiosis and spore formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a CDC28-independent fashion.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jan;22(1):57-68. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.1.57-68.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11739722 Free PMC article.
-
A phosphorylation-independent role for the yeast cyclin-dependent kinase activating kinase Cak1.Gene. 2009 Nov 15;447(2):97-105. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.07.016. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19647054 Free PMC article.
-
The cell cycle rallies the transcription cycle: Cdc28/Cdk1 is a cell cycle-regulated transcriptional CDK.Transcription. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):3-6. doi: 10.4161/trns.22456. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23131667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Cdc28 cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity during the cell cycle of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998 Dec;62(4):1191-243. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.62.4.1191-1243.1998. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9841670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic analysis of the relationship between activation loop phosphorylation and cyclin binding in the activation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc28p cyclin-dependent kinase.Genetics. 2000 Apr;154(4):1549-59. doi: 10.1093/genetics/154.4.1549. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10747052 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinases: Masters of the eukaryotic universe.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Sep 17;15(1):e1816. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1816. Online ahead of print. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 37718413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The plant-specific kinase CDKF;1 is involved in activating phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinases in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2004 Nov;16(11):2954-66. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.025601. Epub 2004 Oct 14. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 15486101 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal activation by cyclin-dependent kinases 2 and 7 is directed by substrate specificity determinants outside the T loop.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jan;21(1):88-99. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.1.88-99.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11113184 Free PMC article.
-
Kin28 is found within TFIIH and a Kin28-Ccl1-Tfb3 trimer complex with differential sensitivities to T-loop phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;22(5):1288-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.5.1288-1297.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11839796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amon A, Tyers M, Futcher B, Nasmyth K. Mechanisms that help the yeast cell cycle clock tick—G2 cyclins transcriptionally activate G2 cyclins and repress G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993;74:993–1007. - PubMed
-
- Andrews B, Measday V. The cyclin family of budding yeast: abundant use of a good idea. Trends Genet. 1998;14:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Chun K T, Goebl M G. Mutational analysis of Cak1p, an essential protein kinase that regulates cell cycle progression. Mol Gen Genet. 1997;256:365–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
