The middle subunit of replication protein A contacts growing RNA-DNA primers in replicating simian virus 40 chromosomes
- PMID: 9774655
- PMCID: PMC109225
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.11.6399
The middle subunit of replication protein A contacts growing RNA-DNA primers in replicating simian virus 40 chromosomes
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol 1999 Jan;19(1):957
Abstract
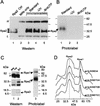
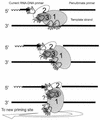
The eukaryotic single-stranded DNA binding protein replication protein A (RPA) participates in major DNA transactions. RPA also interacts through its middle subunit (Rpa2) with regulators of the cell division cycle and of the response to DNA damage. A specific contact between Rpa2 and nascent simian virus 40 DNA was revealed by in situ UV cross-linking. The dynamic attributes of the cross-linked DNA, its size distribution, its RNA primer content, and its replication fork polarity were determined [corrected]. These data suggest that Rpa2 contacts the early DNA chain intermediates synthesized by DNA polymerase alpha-primase (RNA-DNA primers) but not more advanced products. Possible signaling functions of Rpa2 are discussed, and current models of eukaryotic lagging-strand DNA synthesis are evaluated in view of our results.
Figures
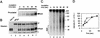
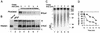
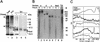
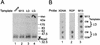
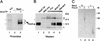
Similar articles
-
Replication protein A modulates its interface with the primed DNA template during RNA-DNA primer elongation in replicating SV40 chromosomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Sep 15;29(18):3892-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.18.3892. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11557822 Free PMC article.
-
Species specificity of human RPA in simian virus 40 DNA replication lies in T-antigen-dependent RNA primer synthesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Dec 1;28(23):4742-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.23.4742. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 11095685 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-protein interactions of the primase subunits p58 and p48 with simian virus 40 T antigen are required for efficient primer synthesis in a cell-free system.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 9;275(23):17328-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000717200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10747950
-
Studies on the initiation of simian virus 40 replication in vitro: RNA primer synthesis and its elongation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):952-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.952. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992. PMID: 1310541 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interactions between SV40 T antigen and other replication proteins at the replication fork.J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11008-17. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8098707
Cited by
-
In the simian virus 40 in vitro replication system, start site selection by the polymerase alpha-primase complex is not significantly altered by changes in the concentration of ribonucleotides.J Virol. 2001 Jul;75(14):6392-401. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.14.6392-6401.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11413306 Free PMC article.
-
Replication protein A binds RNA and promotes R-loop formation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 9;295(41):14203-14213. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013812. Epub 2020 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32796030 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking LBH expression causes replication stress and sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer cells to ATR inhibitor treatment.Oncogene. 2024 Mar;43(12):851-865. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-02951-3. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38297083
-
Binary system for selective photoaffinity labeling of base excision repair DNA polymerases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jul 15;30(14):e73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnf073. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 12136121 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the RPA trimerization core and its role in the multistep DNA-binding mechanism of RPA.EMBO J. 2002 Apr 2;21(7):1855-63. doi: 10.1093/emboj/21.7.1855. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 11927569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bochkarev A, Pfuetzner R A, Edwards A M, Frappier L. Structure of the single-stranded-DNA-binding domain of replication protein A bound to DNA. Nature. 1997;385:176–181. - PubMed
-
- Braun K A, Lao Y, He Z, Ingles C J, Wold M S. Role of protein-protein interactions in the function of replication protein A (RPA): RPA modulates the activity of DNA polymerase alpha by multiple mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1997;36:8443–8454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
