The middle subunit of replication protein A contacts growing RNA-DNA primers in replicating simian virus 40 chromosomes
- PMID: 9774655
- PMCID: PMC109225
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.11.6399
The middle subunit of replication protein A contacts growing RNA-DNA primers in replicating simian virus 40 chromosomes
Erratum in
- Mol Cell Biol 1999 Jan;19(1):957
Abstract
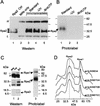
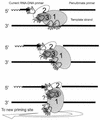
The eukaryotic single-stranded DNA binding protein replication protein A (RPA) participates in major DNA transactions. RPA also interacts through its middle subunit (Rpa2) with regulators of the cell division cycle and of the response to DNA damage. A specific contact between Rpa2 and nascent simian virus 40 DNA was revealed by in situ UV cross-linking. The dynamic attributes of the cross-linked DNA, its size distribution, its RNA primer content, and its replication fork polarity were determined [corrected]. These data suggest that Rpa2 contacts the early DNA chain intermediates synthesized by DNA polymerase alpha-primase (RNA-DNA primers) but not more advanced products. Possible signaling functions of Rpa2 are discussed, and current models of eukaryotic lagging-strand DNA synthesis are evaluated in view of our results.
Figures
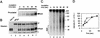
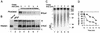
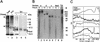
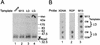
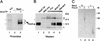
References
-
- Bochkarev A, Pfuetzner R A, Edwards A M, Frappier L. Structure of the single-stranded-DNA-binding domain of replication protein A bound to DNA. Nature. 1997;385:176–181. - PubMed
-
- Braun K A, Lao Y, He Z, Ingles C J, Wold M S. Role of protein-protein interactions in the function of replication protein A (RPA): RPA modulates the activity of DNA polymerase alpha by multiple mechanisms. Biochemistry. 1997;36:8443–8454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
