Cell cycle-regulated expression of mammalian CDC6 is dependent on E2F
- PMID: 9774682
- PMCID: PMC109252
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.11.6679
Cell cycle-regulated expression of mammalian CDC6 is dependent on E2F
Abstract
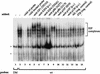
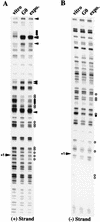
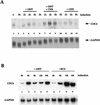
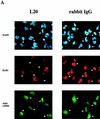
The E2F transcription factors are essential regulators of cell growth in multicellular organisms, controlling the expression of a number of genes whose products are involved in DNA replication and cell proliferation. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the MBF and SBF transcription complexes have functions similar to those of E2F proteins in higher eukaryotes, by regulating the timed expression of genes implicated in cell cycle progression and DNA synthesis. The CDC6 gene is a target for MBF and SBF-regulated transcription. S. cerevisiae Cdc6p induces the formation of the prereplication complex and is essential for initiation of DNA replication. Interestingly, the Cdc6p homolog in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Cdc18p, is regulated by DSC1, the S. pombe homolog of MBF. By cloning the promoter for the human homolog of Cdc6p and Cdc18p, we demonstrate here that the cell cycle-regulated transcription of this gene is dependent on E2F. In vivo footprinting data demonstrate that the identified E2F sites are occupied in resting cells and in exponentially growing cells, suggesting that E2F is responsible for downregulating the promoter in early phases of the cell cycle and the subsequent upregulation when cells enter S phase. Our data also demonstrate that the human CDC6 protein (hCDC6) is essential and limiting for DNA synthesis, since microinjection of an anti-CDC6 rabbit antiserum blocks DNA synthesis and CDC6 cooperates with cyclin E to induce entry into S phase in cotransfection experiments. Furthermore, E2F is sufficient to induce expression of the endogenous CDC6 gene even in the absence of de novo protein synthesis. In conclusion, our results provide a direct link between regulated progression through G1 controlled by the pRB pathway and the expression of proteins essential for the initiation of DNA replication.
Figures
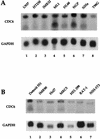

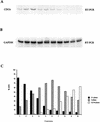



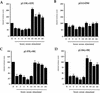






References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: Greene Publishing Associates & Wiley-Interscience; 1988.
-
- Beijersbergen R L, Bernards R. Cell cycle regulation by the retinoblastoma family of growth inhibitory proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1287:103–120. - PubMed
-
- Beijersbergen R L, Kerkhoven R M, Zhu L, Carlée L, Voorhoeve P M, Bernards R. E2F-4, a new member of the E2F gene family, has oncogenic activity and associates with p107 in vivo. Genes Dev. 1994;8:2680–2690. - PubMed
-
- Bell S P, Mitchell J, Leber J, Kobayashi R, Stillman B. The multidomain structure of Orc1p reveals similarity to regulators of DNA replication and transcriptional silencing. Cell. 1995;83:563–568. - PubMed
-
- Bell S P, Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992;357:128–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
