Recombination hotspot activity of hypervariable minisatellite DNA requires minisatellite DNA binding proteins
- PMID: 9776980
- PMCID: PMC3151739
- DOI: 10.1007/BF02677494
Recombination hotspot activity of hypervariable minisatellite DNA requires minisatellite DNA binding proteins
Abstract
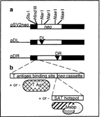
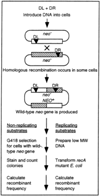
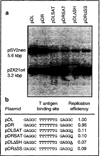
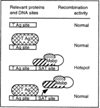
Hypervariable minisatellite DNA repeats are found at tens of thousands of loci in the mammalian genome. These sequences stimulate homologous recombination in mammalian cells [Cell 60:95-103]. To test the hypothesis that protein-DNA interaction is required for hotspot function in vivo, we determined whether a second protein binding nearby could abolish hotspot activity. Intermolecular recombination between pairs of plasmid substrates was measured in the presence or absence of the cis-acting recombination hotspot and in the presence or absence of the second trans-acting DNA binding protein. Minisatellite DNA had hotspot activity in two cell lines, but lacked hotspot activity in two closely related cell lines expressing a site-specific helicase that bound to DNA adjacent to the hotspot. Suppression of hotspot function occurred for both replicating and non-replicating recombination substrates. These results indicate that hotspot activity in vivo requires site occupancy by minisatellite DNA binding proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypervariable minisatellite DNA is a hotspot for homologous recombination in human cells.Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):95-103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90719-u. Cell. 1990. PMID: 2295091
-
Meiotic recombination hotspots: shaping the genome and insights into hypervariable minisatellite DNA change.Curr Top Dev Biol. 1998;37:37-75. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60171-4. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9352183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two hypervariable minisatellite DNA binding proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3269-74. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3269. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991. PMID: 2062643 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous recombination enhancement conferred by the Z-DNA motif d(TG)30 is abrogated by simian virus 40 T antigen binding to adjacent DNA sequences.Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):794-800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.794-800.1990. Mol Cell Biol. 1990. PMID: 2153923 Free PMC article.
-
Human minisatellites, repeat DNA instability and meiotic recombination.Electrophoresis. 1999 Jun;20(8):1665-75. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1522-2683(19990101)20:8<1665::AID-ELPS1665>3.0.CO;2-L. Electrophoresis. 1999. PMID: 10435430 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between simple sequence repeat-rich chromosome regions and intergenomic translocation breakpoints in natural populations of allopolyploid wild wheats.Ann Bot. 2011 Jan;107(1):65-76. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcq215. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Ann Bot. 2011. PMID: 21036694 Free PMC article.
-
DNA sequence-mediated, evolutionarily rapid redistribution of meiotic recombination hotspots.Genetics. 2011 Nov;189(3):685-94. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.134130. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 22084420 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
