The clinicopathological features of gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability may be mediated by mutations of different "target genes": a study of the TGFbeta RII, IGFII R, and BAX genes
- PMID: 9777952
- PMCID: PMC1853052
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65665-9
The clinicopathological features of gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability may be mediated by mutations of different "target genes": a study of the TGFbeta RII, IGFII R, and BAX genes
Abstract
Gastric carcinomas with DNA replication errors (RER phenotype) display a particular clinicopathologic profile and carry a putative favorable prognosis. The RER phenotype has been identified as microsatellite instability in noncoding regions, as well as in repeat sequences within exons of several "target genes": TGFbeta RII, IGFII R, and BAX. In an attempt to find out whether the RER status is a significant prognostic factor in gastric carcinoma in a multivariate analysis and whether the clinicopathological features of the RER+ tumors are associated with mutations in the "target genes," we evaluated a series of 152 cases of sporadic gastric carcinoma. Five or six microsatellite loci and/or BAT 26, a poly(A) tract, were analyzed in each case using polymerase chain reaction and electrophoresis. Thirty-five cases (23.0%) were RER+. The RER phenotype was closely associated with a low pTNM stage and carried a significantly better prognosis. The repeat sequences of the target genes were screened for mutations in 28 RER+ and 13 RER-tumors. Mutations in TGFbeta RII occurred in 67.9% of the RER+ tumors and were significantly associated with the glandular histotype. IGFII R and BAX mutations occurred, respectively, in 25.0% and 32.1% of the cases; there was a trend toward an association between mutations in these genes and decreased nodal metastization and wall invasiveness, respectively. We conclude that the RER status is a significant prognostic indicator in gastric carcinoma and that such prognostic influence may be mediated by mutations in TGFbeta RII, IGFII R, and BAX genes.
Figures
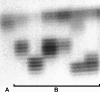
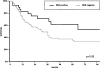

References
-
- Hoang JM, Cottu PH, Thuille B, Salmon RJ, Thomas G, Hamelin R: BAT-26, an indicator of the replication error phenotype in colorectal cancers cell lines. Cancer Res 1997, 57:300-303 - PubMed
-
- Thibodeau SN, Bren G, Schaid D: Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science 1993, 260:816-819 - PubMed
-
- Ionov Y, Peinado MA, Malkhosyan S, Shibata D, Perucho M: Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature 1993, 363:558-561 - PubMed
-
- Risinger JI, Umar A, Barrett JC, Kunkel TA: A hPMS2 mutant cell line in defective in strand-specific mismatch repair. J Biol Chem 1995, 270:18183-18186 - PubMed
-
- Santos NR, Seruca R, Constância M, Seixas M, Sobrinho-Simões M: Microsatellite instability at multiple loci in gastric carcinoma: clinicopathologic implications and prognosis. Gastroenterology 1996, 110:38-44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

