Human interleukin-10 expression in T/natural killer-cell lymphomas: association with anaplastic large cell lymphomas and nasal natural killer-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 9777954
- PMCID: PMC1853048
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65667-2
Human interleukin-10 expression in T/natural killer-cell lymphomas: association with anaplastic large cell lymphomas and nasal natural killer-cell lymphomas
Abstract
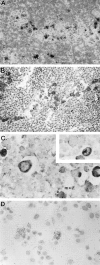
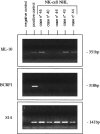
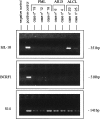
Several cytokines have been implicated in the pathogenesis of human lymphomas. Among them, interleukin-10 (IL-10) is a pleiotropic cytokine with various biological effects on B and T lymphocytes. Its expression has been essentially studied in B-cell lymphomas, where it appears to act as an autocrine growth factor. BCRF1 (also called viral IL-10), an open reading frame of Epstein-Barr virus, exhibits extensive sequence and functional homologies with human IL-10. Some entities belonging to T- or natural killer (NK)-cell lymphomas are characterized by a frequent association with Epstein-Barr virus. We analyzed 39 cases of peripheral T-cell lymphoma, as well as 7 cases of nasal NK-cell lymphoma, for the presence of IL-10 transcripts by in situ hybridization, to see whether this cytokine was expressed in these tumors and whether its expression could be related to their histological subtype and to the presence of Epstein-Barr virus. Because the riboprobe used for in situ hybridization recognizes both human and viral IL-10, 12 cases were also analyzed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction to verify the human or viral origin of IL-10. It was found that 8 of 11 (73%) anaplastic large cell lymphomas (ALCLs), 2 of 11 (18%) pleomorphic T-cell lymphomas, and 3 of 7 (43%) nasal NK-cell lymphomas exhibited a large number of IL-10-expressing cells, whereas only rare scattered cells were detected in angioimmunoblastic (11 of 11) and in gammadelta T-cell lymphomas (6 of 6). In ALCLs, the pattern of IL-10 mRNA-expressing cells showed an overlapping with the CD30 staining and preferential localization in sinusal and perifollicular areas, thereby suggesting that IL-10-expressing cells were tumor cells. Furthermore, IL-10 transcripts were detected in the SU-DHL-1 anaplastic lymphoma cell line. No correlation with Epstein-Barr virus profile was found, because all cases of ALCL were negative for EBER 1 and 2 genes by in situ hybridization. We confirmed the presence of human IL-10 mRNA by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in ALCLs as well as in NK-cell lymphomas, whereas viral IL-10 was not detected. Thus, human and not viral IL-10 is frequently expressed by tumor cells in ALCLs and nasal NK-cell lymphomas. In view of its function in the proliferation and the differentiation of cytotoxic T and NK cells, and its immunosuppressive properties, IL-10 may have a role in the pathogenesis of these lymphomas.
Figures

References
-
- Hsu SM, Waldron JW, Hsu PL, Hough AJ: Cytokines in malignant lymphomas: review and perspective evaluation. Hum Pathol 1993, 24:1040-1057 - PubMed
-
- Pistoia V: Production of cytokines by human B cell in health and disease. Immunol Today 1997, 18:343-350 - PubMed
-
- Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM, Chan JKC, Cleary ML, Delsol G, De Wolf-Peters C, Falini B, Gatter KC, Grogan TM, Isaacson PG, Knowles DM, Mason DY, Müller-Hermelink HK, Pileri SA, Piris MA, Ralfkiaer E, Warnke RA: A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994, 84:1361-1392 - PubMed
-
- Gaulard P, Bourquelot P, Kanavaros P, Haioun C, Le Couedic JP, Divine M, Goossens M, Zafrani ES, Farcet JP, Reyes F: Expression of the α/β and γ/δ T-cell receptors in 57 cases of peripheral T-cell lymphomas: identification of a subset of γδ T-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol 1990, 137:617-628 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Foss HD, Anagnostopoulos I, Herbst H, Grebe M, Ziemann K, Hummel M, Stein H: Patterns of cytokine gene expression in peripheral T-cell lymphoma of angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy type. Blood 1995, 10:2862-2869 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

