Spontaneous electrical rhythmicity in cultured interstitial cells of cajal from the murine small intestine
- PMID: 9782170
- PMCID: PMC2231277
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.203by.x
Spontaneous electrical rhythmicity in cultured interstitial cells of cajal from the murine small intestine
Abstract
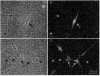
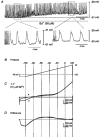
1. Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) are pacemaker cells in the small bowel, and therefore this cell type must express the mechanism responsible for slow wave activity. Isolated ICC were cultured for 1-3 days from the murine small intestine and identified with c-Kit-like immunoreactivity (c-Kit-LI). 2. Electrical recordings were obtained from cultured ICC with the whole-cell patch clamp technique. ICC were rhythmically active, producing regular slow wave depolarizations with waveforms and properties similar to slow waves in intact tissues. 3. Spontaneous activity of c-Kit-LI cells was inhibited by reduced extracellular Na+, gadolinium, and reduced extracellular Ca2+. The activity was not affected by nisoldipine. Voltage clamp studies showed rhythmic inward currents that were probably responsible for the slow wave activity. The current-voltage relationship showed that the spontaneous currents reversed at about +17 mV. These observations are consistent with the involvement of a non-selective cation current in the generation of slow waves, but do not rule out contributions from other conductances or transporters. 4. A Ba2+-sensitive inwardly rectifying K+ current in c-Kit-LI cells that may be involved in slow wave repolarization and maintenance of a negative potential between slow waves was also found. Similar pharmacology was observed in studies of intact murine intestinal muscles. 5. Cultured ICC may be a useful model for studying the properties and pharmacology of some of the ionic conductances involved in spontaneous rhythmicity in the gastrointestinal tract.
Figures




References
-
- Burns AJ, Herbert TM, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract as revealed by c-Kit immunohistochemistry. Cell and Tissue Research. 1997;290:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Cayabyab FS, deBruin H, Jimenez M, Daniel EE. Ca2+ role in myogenic and neurogenic activities of canine ileum circular muscle. American Journal of Physiology. 1996;271:G1053–1066. - PubMed
-
- El-Sharkawy TY, Daniel EE. Ionic mechanisms of intestinal electrical control activity. American Journal of Physiology. 1975;229:1287–1298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

