mRNA stabilization by poly(A) binding protein is independent of poly(A) and requires translation
- PMID: 9784497
- PMCID: PMC317214
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.20.3226
mRNA stabilization by poly(A) binding protein is independent of poly(A) and requires translation
Abstract
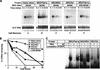
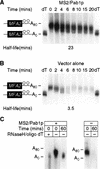
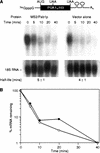
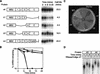
Translation and mRNA stability are enhanced by the presence of a poly(A) tail. In vivo, the tail interacts with a conserved polypeptide, poly(A) binding protein (Pab1p). To examine Pab1p function in vivo, we have tethered Pab1p to the 3' UTR of reporter mRNAs by fusing it to MS2 coat protein and placing MS2 binding sites in the 3' UTR of the reporter. This strategy allows us to uncouple Pab1p function from its RNA binding activity. We show that mRNAs that lack a poly(A) tail in vivo are stabilized by Pab1p, and that the portions of Pab1p required for stabilization are genetically distinct from those required for poly(A) binding. In addition, stabilization by Pab1p requires ongoing translation of the mRNA. We conclude that the primary, or sole, function of poly(A) with respect to mRNA stability is simply to bring Pab1p to the mRNA, and that mRNA stabilization is an intrinsic property of Pab1p. The approach we describe may be useful in identifying and assaying 3' UTR regulatory proteins, as it uncouples analysis of function from RNA binding.
Figures



References
-
- Beelman C, Parker R. Differential effects of translational inhibition in cis and in trans on the decay of the unstable yeast MFA2 mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:9687–9692. - PubMed
-
- Beelman C, Stevens A, Caponigro G, Lagrandeur T, Hatfield L, Fortner D, Parker R. An essential component of the decapping enzyme required for normal rates of mRNA turnover. Nature. 1996;382:642–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
