Drosophila unpaired encodes a secreted protein that activates the JAK signaling pathway
- PMID: 9784499
- PMCID: PMC317220
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.20.3252
Drosophila unpaired encodes a secreted protein that activates the JAK signaling pathway
Abstract
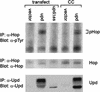
In vertebrates, many cytokines and growth factors have been identified as activators of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. In Drosophila, JAK and STAT molecules have been isolated, but no ligands or receptors capable of activating the pathway have been described. We have characterized the unpaired (upd) gene, which displays the same distinctive embryonic mutant defects as mutations in the Drosophila JAK (hopscotch) and STAT (stat92E) genes. Upd is a secreted protein, associated with the extracellular matrix, that activates the JAK pathway. We propose that Upd is a ligand that relies on JAK signaling to stimulate transcription of pair-rule genes in a segmentally restricted manner in the early Drosophila embryo.
Figures






References
-
- Ashburner M. Drosophila: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989.
-
- Binari R, Perrimon N. Stripe-specific regulation of pair-rule genes by hopscotch, a putative Jak family tyrosine kinase in Drosophila. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:300–312. - PubMed
-
- Brown NH, Kafatos FC. Functional cDNA libraries from Drosophila embryos. J Mol Biol. 1988;203:425–437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
