Staphylococcal enterotoxin B primes cytokine secretion and lytic activity in response to native bacterial antigens
- PMID: 9784507
- PMCID: PMC108633
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5082-5088.1998
Staphylococcal enterotoxin B primes cytokine secretion and lytic activity in response to native bacterial antigens
Abstract
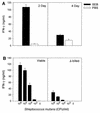
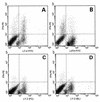
Superantigens stimulate T-lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production, but the effects of superantigen exposure on cell function within a complex, highly regulated immune response remain to be determined. In this study, we demonstrate that superantigen exposure significantly alters the murine host response to bacterial antigens in an in vitro coculture system. Two days after exposure to the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B, splenocytes cultured with Streptococcus mutans produced significantly greater amounts of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and interleukin-12 than did sham-injected controls. The majority of IFN-gamma production appeared to be CD8(+) T-cell derived since depletion of this cell type dramatically reduced the levels of IFN-gamma. To study host cell damage that may occur following superantigen exposure, we analyzed cytotoxicity to "bystander" fibroblast cells cultured with splenocytes in the presence of bacterial antigens. Prior host exposure to staphylococcal enterotoxin B significantly enhanced fibroblast cytotoxicity in the presence of bacteria. Neutralization of IFN-gamma decreased the amount of cytotoxicity observed. However, a greater reduction was evident when splenocyte-bacterium cocultures were separated from the bystander cell monolayer via a permeable membrane support. Increased cytotoxicity appears to be primarily dependent upon cell-cell contact. Collectively, these data indicate that overproduction of inflammatory cytokines may alter the activity of cytotoxic immune cells. Superantigen exposure exacerbates cytokine production and lytic cell activity when immune cells encounter bacteria in vitro and comparable activities could possibly occur in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of a novel in vitro co-culture system for studying host response to native bacterial antigens.J Immunol Methods. 1998 Feb 1;211(1-2):147-58. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(97)00200-7. J Immunol Methods. 1998. PMID: 9617839
-
Superantigenic staphylococcal exotoxins induce T-cell proliferation in the presence of Langerhans cells or class II-bearing keratinocytes and stimulate keratinocytes to produce T-cell-activating cytokines.J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Jan;102(1):31-8. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12371727. J Invest Dermatol. 1994. PMID: 8288908
-
Activation of mouse liver natural killer cells and NK1.1(+) T cells by bacterial superantigen-primed Kupffer cells.Hepatology. 1999 Aug;30(2):430-6. doi: 10.1002/hep.510300209. Hepatology. 1999. PMID: 10421651
-
CD8+ cells are the main producers of IL10 and IFN gamma after superantigen stimulation.Scand J Immunol. 1996 Nov;44(5):501-5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1996.d01-339.x. Scand J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8947602
-
Mycobacterium bovis BCG-infected mice are more susceptible to staphylococcal enterotoxin B-mediated toxic shock than uninfected mice despite reduced in vitro splenocyte responses to superantigens.Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4148-57. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4148-4157.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117923 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Disrupts Endothelial-Cell Tight Junctions via Acid Sphingomyelinase and Ceramide.Infect Immun. 2017 Dec 19;86(1):e00606-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00606-17. Print 2018 Jan. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 29084896 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Post-Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B Exposure Protects Mice From Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Toxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 16;11:893. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00893. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32612530 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of superantigens protects mice from lethal Listeria monocytogenes infection by enhancing cytotoxic T cells.Infect Immun. 2001 Nov;69(11):6633-42. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.6633-6642.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11598032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aste-Amezaga M, D’Andrea A, Kubin M, Trinchieri G. Cooperation of natural killer cell stimulatory factor/interleukin-12 with other stimuli in the induction of cytokines and cytotoxic cell-associated molecules in human T and NK cells. Cell Immunol. 1994;156:480–492. - PubMed
-
- Avery A, Markowitz J, Grusby M, Glimcher L, Cantor H. Activation of T cells by superantigen in class II-negative mice. J Immunol. 1994;153:4853–4861. - PubMed
-
- Bell S, Vroegop S, Buxser S. Early activation and cell trafficking induced by staphylococcal enterotoxin B: effects of high- versus low-dose challenge on induction of anergy. Cell Immunol. 1994;154:440–452. - PubMed
-
- Bell S, Buxser S. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B modulates Vβ8 TCR-associated T-cell memory against conventional antigen. Cell Immunol. 1995;160:58–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

