Activation of Rho GTPases by Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 increases intestinal permeability in Caco-2 cells
- PMID: 9784513
- PMCID: PMC108639
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5125-5131.1998
Activation of Rho GTPases by Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 increases intestinal permeability in Caco-2 cells
Abstract
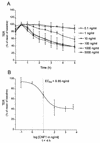
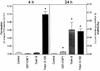
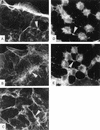
The cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1) activates Rho GTPases by deamidation of glutamine-63 and thereby induces redistribution of the actin cytoskeleton and formation of stress fibers. Here, we have studied the effects of CNF1 on the transepithelial resistance of Caco-2 cells, a human intestinal epithelial cell line, in comparison with the Rho-inactivating toxin B of Clostridium difficile. Whereas toxin B decreased the transepithelial resistance of Caco-2 cells by about 80% after 4 h, CNF1 reduced it by about 40%. Significant changes of the transepithelial resistance induced by CNF1 were detected after 3 h of incubation. Half-maximal effects were observed with 10 and 41 ng of CNF1 and toxin B per ml, respectively. Flux measurement revealed no CNF1-induced increase of fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran permeation within the first 4 h of incubation and a 2.9-fold increase after 24 h of incubation. In contrast, toxin B induced a 28-fold increase of permeation after 24 h. As detected by rhodamine-phalloidin staining, CNF1 increased polymerization of F actin at focal contacts of adjacent cells and induced formation of stress fibers. The data indicate that not only depolymerization but also polymerization of actin and subsequent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton alter the barrier function of intestinal tight junctions.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1), a toxin that activates the Rho GTPase.J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 1;272(31):19532-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.31.19532. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9235957
-
Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 effaces microvilli and decreases transmigration of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in intestinal T84 epithelial cell monolayers.Infect Immun. 1998 Jun;66(6):2494-500. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.6.2494-2500.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9596707 Free PMC article.
-
Differential role of Rho GTPases in intestinal epithelial barrier regulation in vitro.J Cell Physiol. 2011 May;226(5):1196-203. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22446. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20945370
-
The cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1) from Escherichia coli.Toxicon. 2001 Nov;39(11):1673-80. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(01)00154-4. Toxicon. 2001. PMID: 11595630 Review.
-
Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 from Escherichia coli: a toxin with a new intracellular activity for eukaryotic cells.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1998;43(3):285-9. doi: 10.1007/BF02818614. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 1998. PMID: 9717256 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Rho GTPases in Toxicity of Clostridium difficile Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2015 Dec 2;7(12):5254-67. doi: 10.3390/toxins7124874. Toxins (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26633511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Escherichia coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 on repair of human bladder cell monolayers in vitro.Infect Immun. 1999 Jul;67(7):3657-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.7.3657-3661.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10377155 Free PMC article.
-
Making Sense of Quorum Sensing at the Intestinal Mucosal Interface.Cells. 2022 May 24;11(11):1734. doi: 10.3390/cells11111734. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cytotoxic necrotizing factor of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (CNFY) enhances inflammation and Yop delivery during infection by activation of Rho GTPases.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(11):e1003746. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003746. Epub 2013 Nov 7. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24244167 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the Endosomal Anion/Proton Exchanger ClC-5 Increases Cell Susceptibility toward Clostridium difficile Toxins TcdA and TcdB.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Mar 13;7:67. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00067. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28348980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aktories K, Braun U, Rösener S, Just I, Hall A. The rho gene product expressed in E. coli is a substrate of botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;158:209–213. - PubMed
-
- Braun U, Habermann B, Just I, Aktories K, Vandekerckhove J. Purification of the 22 kDa protein substrate of botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferase C3 from porcine brain cytosol and its characterization as a GTP-binding protein highly homologous to the rho gene product. FEBS Lett. 1989;243:70–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

