Immunological characterization of Asp f 2, a major allergen from Aspergillus fumigatus associated with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 9784519
- PMCID: PMC108645
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5175-5182.1998
Immunological characterization of Asp f 2, a major allergen from Aspergillus fumigatus associated with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
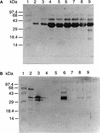
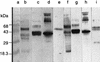
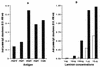
The 37-kDa recombinant protein Asp f 2, encoding an allergen of Aspergillus fumigatus, was expressed in a prokaryotic expression system and immunologically evaluated for its functional and structural properties. The open reading frame for a 310-amino-acid-long protein was shown to encode a signal peptide of 31 amino acids. A native 37-kDa culture filtrate protein and a 55-kDa mycelial glycoprotein (gp55) exhibited complete N-terminal sequence homology to Asp f 2. A GenBank search for homologous proteins revealed 60 and 44% sequence homologies to the cytosolic protein ASPND1 from Aspergillus nidulans and fibrinogen binding protein from Candida albicans, respectively. The glycosylation sites and cysteine molecules are conserved in all the three proteins. The extracellular matrix protein laminin showed a dose-dependent interaction with Asp f 2. This protein, expressed as a major cell-associated protein within 24 h of in vitro fungal culture, comprises 20 to 40% of total fungal protein. Furthermore, both native and recombinant Asp f 2 exhibited specific immunoglobulin (IgE) binding with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) and cystic fibrosis-ABPA patients, whereas A. fumigatus-sensitized allergic asthma and normal control subjects failed to show IgE binding with Asp f 2. These results indicate that Asp f 2 is a major allergen of A. fumigatus exhibiting IgE antibody binding with sera from patients with ABPA. The antigen should be explored further for its potential role in the differential diagnosis of A. fumigatus-associated allergic diseases.
Figures



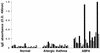
References
-
- Arruda L K, Mann B J, Chapman M D. Selective expression of a major allergen and cytotoxin, Asp f I, in Aspergillus fumigatus. Implications for the immunopathogenesis of Aspergillus-related diseases. J Immunol. 1992;149:3354–3359. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee B, Kurup V P, Greenberger P A, Hoffman D R, Nair D S, Fink J N. Purification of a major allergen, Asp f 2 binding to IgE in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, from culture filtrate of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;99:821–827. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee B, Kurup V P, Phadnis S, Greenberger P A, Fink J N. Molecular cloning and expression of a recombinant Aspergillus fumigatus protein AspfII with significant immunoglobulin E reactivity in allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1996;127:253–262. - PubMed
-
- Bardana E J., Jr The clinical spectrum of aspergillosis. Part 1. Epidemiology, pathogenicity, infection in animals and immunology of aspergillosis. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1981;13:21–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

