Oral immunization with a Salmonella typhimurium vaccine vector expressing recombinant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K99 fimbriae elicits elevated antibody titers for protective immunity
- PMID: 9784559
- PMCID: PMC108685
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5470-5476.1998
Oral immunization with a Salmonella typhimurium vaccine vector expressing recombinant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K99 fimbriae elicits elevated antibody titers for protective immunity
Abstract
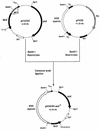
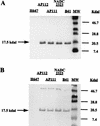
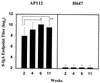
Bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) continues to cause mortality in piglets and newborn calves. In an effort to develop a safe and effective vaccine for the prevention of F5(+) ETEC infections, a balanced lethal asd+ plasmid carrying the complete K99 operon was constructed and designated pMAK99-asd+. Introduction of this plasmid into an attenuated Salmonella typhimurium Deltaaro Deltaasd strain, H683, resulted in strain AP112, which stably expresses E. coli K99 fimbriae. A single oral immunization of BALB/c and CD-1 mice with strain AP112 elicited significant mucosal immunoglobulin A (IgA) titers that remained elevated for >11 weeks. IgA and IgG responses in serum specific for K99 fimbriae were also induced, with a prominent IgG1, as well as IgG2a and IgG2b, titer. To assess the derivation of these antibodies, a K99 isotype-specific B-cell ELISPOT analysis was conducted by using mononuclear cells from the lamina propria of the small intestines (LP), Peyer's patches (PP), and spleens of vaccinated and control BALB/c mice. This analysis revealed elevated numbers of K99 fimbria-specific IgA-producing cells in the LP, PP, and spleen, whereas elevated K99 fimbria-specific IgG-producing cells were detected only in the PP and spleen. These antibodies were important for protective immunity. One-day-old neonates from dams orally immunized with AP112 were provided passive protection against oral challenge with wild-type ETEC, in contrast to challenged neonates from unvaccinated dams or from dams vaccinated with a control Salmonella vector. These results confirm that oral Salmonella vaccine vectors effectively deliver K99 fimbriae to mucosal inductive sites for sustained elevation of IgA and IgG antibodies and for eliciting protective immunity.
Figures
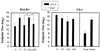


References
-
- Attridge S R, Hackett J, Morona R, Whyte P. Towards a live oral vaccine against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of swine. Vaccine. 1988;6:387–389. - PubMed
-
- Attridge S R, Davies R, LaBrooy J T. Oral delivery of foreign antigens by attenuated Salmonella: consequences of prior exposure to the vector strain. Vaccine. 1997;15:155–162. - PubMed
-
- Bertram E M, Attridge S R, Kotlarski I. Immunogenicity of the Escherichia coli fimbrial antigen K99 when expressed by Salmonella enteritidis 11RX. Vaccine. 1994;12:1372–1378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

