Murine model of Bartonella henselae infection in the immunocompetent host
- PMID: 9784568
- PMCID: PMC108694
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5534-5536.1998
Murine model of Bartonella henselae infection in the immunocompetent host
Abstract
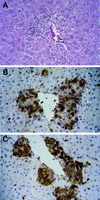
Bartonella henselae is an emerging pathogen causing cat scratch disease, bacillary angiomatosis, and peliosis hepatis. Progress in understanding the pathogenesis of and the immune response to these infections has been limited by the lack of an animal model. Following intraperitoneal infection of C57BL/6 mice with B. henselae, organs were cleared of cultivatable bacteria within 6 days. In contrast, B. henselae DNA could be detected in liver tissue for at least 3 months. Liver tissue showed granulomatous inflammation reaching its highest degree of intensity during the fourth week of infection and resolving within 12 weeks postinfection. This mouse model is applicable to the study of the pathogenesis of B. henselae and the immune response to this pathogen in the immunocompetent host.
Figures

References
-
- Cockerell J C, Connor D H. Cat scratch disease. In: Connor D H, Chandler F W, Schwartz D A, Manz H J, Lack E E, editors. Pathology of infectious diseases. Stamford, Conn: Appleton & Lange; 1979. pp. 461–468.
-
- Dolan M J, Wong M T, Regnery R L, Jorgensen J H, Garcia M, Peters J, Drehner D. Syndrome of Rochalimaea henselae adenitis suggesting cat scratch disease. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118:331–336. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

