Structural and antigenic characteristics of Streptococcus sobrinus glucan binding proteins
- PMID: 9784575
- PMCID: PMC108701
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5565-5569.1998
Structural and antigenic characteristics of Streptococcus sobrinus glucan binding proteins
Abstract
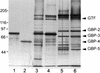
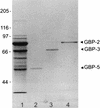
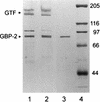
Three purified glucan binding proteins (GBP-2, GBP-3, and GBP-5) from Streptococcus sobrinus 6715 were compared structurally by mass spectroscopy of tryptic fragments and antigenically by Western blot analysis with rat antisera to each GBP or to peptides containing putative glucan binding epitopes of mutans streptococcal glucosyltransferases. Structural and antigenic analyses indicated that GBP-3 and GBP-5 are very similar but that both are essentially unrelated to GBP-2. None of these S. sobrinus GBPs appeared to have a strong antigenic relationship with GBPs from Streptococcus mutans. Thus, S. sobrinus GBP-2 and GBP-3 appear to be distinct proteins with potentially different functions. S. sobrinus GBP-5 may be a proteolytic fragment of GBP-3, or, alternatively, the genes coding for these proteins may be closely related.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

