A protein (M9) associated with monoclonal antibody-mediated agglutination of Mycoplasma gallisepticum is a member of the pMGA family
- PMID: 9784576
- PMCID: PMC108702
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.11.5570-5575.1998
A protein (M9) associated with monoclonal antibody-mediated agglutination of Mycoplasma gallisepticum is a member of the pMGA family
Abstract
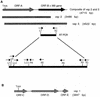
A 62-kDa cell surface antigen (M9) of Mycoplasma gallisepticum PG31 that mediates antibody-induced agglutination of the organism was purified and subjected to N-terminal amino-acid sequencing. A 999-bp region of the cDNA encoding the M9 protein was generated by reverse transcription-PCR, and its nucleotide sequence was determined. PCR primers based on this sequence were used to screen a genomic DNA library of PG31. A full-length M9 protein-encoding gene was isolated and sequenced, revealing 96% nucleotide identity with the pMGA1.1 gene of M. gallisepticum S6. Sequence analyses of the M9 gene and flanking open reading frames that encode other pMGA family members suggest that a tandemly repeated GAA sequence may influence pMGA gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Aebersold R. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. In: Matsudaira P, editor. A practical guide to protein and peptide purification for microsequencing. 2nd ed. San Diego, Calif: Academic Press, Inc.; 1993. pp. 102–124.
-
- Amaravadi L, King M W. A rapid and efficient, nonradioactive method for screening recombinant DNA libraries. BioTechniques. 1994;16:98–103. - PubMed
-
- Baseggio N, Glew M D, Markham P F, Whithear K G, Browning G F. Size and genomic location of the pMGA multigene family of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Microbiology. 1996;142:1429–1435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

