Layilin, a novel talin-binding transmembrane protein homologous with C-type lectins, is localized in membrane ruffles
- PMID: 9786953
- PMCID: PMC2132847
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.143.2.429
Layilin, a novel talin-binding transmembrane protein homologous with C-type lectins, is localized in membrane ruffles
Abstract
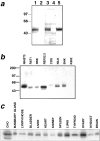
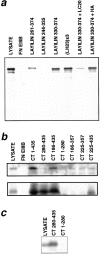
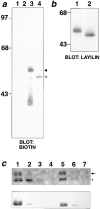
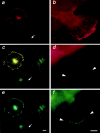
Changes in cell morphology and motility are mediated by the actin cytoskeleton. Recent advances in our understanding of the regulators of microfilament structure and dynamics have shed light on how these changes are controlled, and efforts continue to define all the structural and signaling components involved in these processes. The actin cytoskeleton-associated protein talin binds to integrins, vinculin, and actin. We report a new binding partner for talin that we have named layilin, which contains homology with C-type lectins, is present in numerous cell lines and tissue extracts, and is expressed on the cell surface. Layilin colocalizes with talin in membrane ruffles, and is recruited to membrane ruffles in cells induced to migrate in in vitro wounding experiments and in peripheral ruffles in spreading cells. A ten-amino acid motif in the layilin cytoplasmic domain is sufficient for talin binding. We have identified a short region within talin's amino-terminal 435 amino acids capable of binding to layilin in vitro. This region overlaps a binding site for focal adhesion kinase.
Figures




References
-
- Albigès-Rizo C, Frachet P, Block MR. Down regulation of talin alters cell adhesion and the processing of the α5β1 integrin. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:3317–3329. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RA, Marchesi VT. Regulation of the association of membrane skeletal protein 4.1 with glycophorin by a polyphosphoinositide. Nature. 1985;318:295–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

