Functional differences between keratins of stratified and simple epithelia
- PMID: 9786957
- PMCID: PMC2132837
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.143.2.487
Functional differences between keratins of stratified and simple epithelia
Abstract
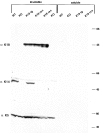
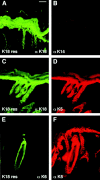
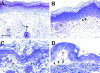
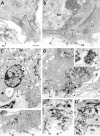
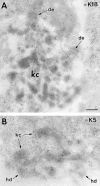
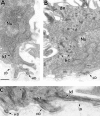
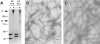
Dividing populations of stratified and simple epithelial tissues express keratins 5 and 14, and keratins 8 and 18, respectively. It has been suggested that these keratins form a mechanical framework important to cellular integrity, since their absence gives rise to a blistering skin disorder in neonatal epidermis, and hemorrhaging within the embryonic liver. An unresolved fundamental issue is whether different keratins perform unique functions in epithelia. We now address this question using transgenic technology to express a K16-14 hybrid epidermal keratin transgene and a K18 simple epithelial keratin transgene in the epidermis of mice null for K14. Under conditions where the hybrid epidermal keratin restored a wild-type phenotype to newborn epidermis, K18 partially but not fully rescued. The explanation does not appear to reside in an inability of K18 to form 10-nm filaments with K5, which it does in vitro and in vivo. Rather, it appears that the keratin network formed between K5 and K18 is deficient in withstanding mechanical stress, leading to perturbations in the keratin network in regions of the skin that are subjected either to natural or to mechanically induced trauma. Taken together, these findings suggest that the loss of a type I epidermal keratin cannot be fully compensated by its counterpart of simple epithelial cells, and that in vivo, all keratins are not equivalent.
Figures
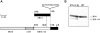

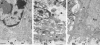
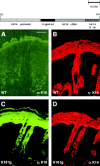
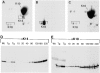
Similar articles
-
Structure and functions of keratin proteins in simple, stratified, keratinized and cornified epithelia.J Anat. 2009 Apr;214(4):516-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01066.x. J Anat. 2009. PMID: 19422428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pairwise assembly determines the intrinsic potential for self-organization and mechanical properties of keratin filaments.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Jan;13(1):382-91. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-10-0522. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11809846 Free PMC article.
-
The functional diversity of epidermal keratins revealed by the partial rescue of the keratin 14 null phenotype by keratin 16.J Cell Biol. 1999 Sep 6;146(5):1185-201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.5.1185. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10477769 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of keratin K14 in the epidermis and hair follicle: insights into complex programs of differentiation.J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2295-312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2295. J Cell Biol. 1989. PMID: 2478566 Free PMC article.
-
Keratin expression by corneal and limbal stem cells during development.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Nov;200:108206. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.108206. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32882212 Review.
Cited by
-
A Maverick Review of Common Stem/Progenitor Markers in Lung Development.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Dec;18(8):2629-2645. doi: 10.1007/s12015-022-10422-z. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 35871209 Review.
-
Structure and functions of keratin proteins in simple, stratified, keratinized and cornified epithelia.J Anat. 2009 Apr;214(4):516-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01066.x. J Anat. 2009. PMID: 19422428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complete cytolysis and neonatal lethality in keratin 5 knockout mice reveal its fundamental role in skin integrity and in epidermolysis bullosa simplex.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jun;12(6):1775-89. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.6.1775. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11408584 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive expression of human keratin 14 gene in mouse lung induces premalignant lesions and squamous differentiation.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Dec;29(12):2377-84. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn190. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18701433 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal Cancer: Insights From Mouse Models.Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2015 Aug 16;8(Suppl 1):37-46. doi: 10.4137/CGM.S21218. eCollection 2015. Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2015. PMID: 26380556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anton-Lamprecht I. Ultrastructural identification of basic abnormalities as clues to genetic disorders of the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1994;103:65–125. - PubMed
-
- Baribault H, Price J, Miyai K, Oshima RG. Mid-gestational lethality in mice lacking keratin 8. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1191–1201. - PubMed
-
- Baribault H, Penner J, Iozzo RV, Wilson-Heiner M. Colorectal hyperplasia and inflammation in keratin 8-deficient FVB/N mice. Genes Dev. 1994;8:2964–2973. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

