Directed evolution of a thermostable esterase
- PMID: 9788996
- PMCID: PMC23604
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.12809
Directed evolution of a thermostable esterase
Abstract
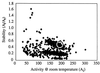
We have used in vitro evolution to probe the relationship between stability and activity in a mesophilic esterase. Previous studies of these properties in homologous enzymes evolved for function at different temperatures have suggested that stability at high temperatures is incompatible with high catalytic activity at low temperatures through mutually exclusive demands on enzyme flexibility. Six generations of random mutagenesis, recombination, and screening stabilized Bacillus subtilis p-nitrobenzyl esterase significantly (>14 degreesC increase in Tm) without compromising its catalytic activity at lower temperatures. Furthermore, analysis of the stabilities and activities of large numbers of random mutants indicates that these properties are not inversely correlated. Although enhanced thermostability does not necessarily come at the cost of activity, the process by which the molecule adapts is important. Mutations that increase thermostability while maintaining low-temperature activity are very rare. Unless both properties are constrained (by natural selection or screening) the evolution of one by the accumulation of single amino acid substitutions typically comes at the cost of the other, regardless of whether the two properties are inversely correlated or not correlated at all.
Figures


References
-
- Jaenicke R, Schurig H, Beaucamp N, Ostendorp R. Adv Protein Chem. 1996;48:181–269. - PubMed
-
- Argos P, Rossman M G, Grau U M, Zuber H, Frank G, Tratschin J D. Biochemistry. 1979;18:5698–5703. - PubMed
-
- Imanaka T, Shibazaki M, Takagi M. Nature (London) 1986;324:695–697. - PubMed
-
- Guez-Ivanier V, Hermann M, Baldwin D, Bedouell H. J Mol Biol. 1993;234:209–221. - PubMed
-
- Matthews B W. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:139–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

