Identification of two distinct human SMC protein complexes involved in mitotic chromosome dynamics
- PMID: 9789013
- PMCID: PMC23650
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.12906
Identification of two distinct human SMC protein complexes involved in mitotic chromosome dynamics
Abstract
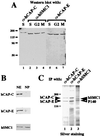
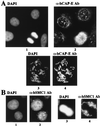
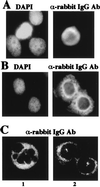
The structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) family member proteins previously were shown to play a critical role in mitotic chromosome condensation and segregation in yeast and Xenopus. Other family members were demonstrated to be required for DNA repair in yeast and mammals. Although several different SMC proteins were identified in different organisms, little is known about the SMC proteins in humans. Here, we report the identification of four human SMC proteins that form two distinct heterodimeric complexes in the cell, the human chromosome-associated protein (hCAP)-C and hCAP-E protein complex (hCAP-C/hCAP-E), and the human SMC1 (hSMC1) and hSMC3 protein complex (hSMC1/hSMC3). The hCAP-C/hCAP-E complex is the human ortholog of the Xenopus chromosome-associated protein (XCAP)-C/XCAP-E complex required for mitotic chromosome condensation. We found that a second complex, hSMC1/hSMC3, is required for metaphase progression in mitotic cells. Punctate vs. diffuse distribution patterns of the hCAP-C/hCAP-E and hSMC1/hSMC3 complexes in the interphase nucleus indicate independent behaviors of the two complexes during the cell cycle. These results suggest that two distinct classes of SMC protein complexes are involved in different aspects of mitotic chromosome organization in human cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A human condensin complex containing hCAP-C-hCAP-E and CNAP1, a homolog of Xenopus XCAP-D2, colocalizes with phosphorylated histone H3 during the early stage of mitotic chromosome condensation.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;20(18):6996-7006. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.18.6996-7006.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10958694 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-dependent expression and nucleolar localization of hCAP-H.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Nov;12(11):3527-37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.11.3527. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11694586 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of hCAP-D2, a non-SMC subunit of condensin I, to chromosome and chromosomal protein dynamics during mitosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;25(2):740-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.2.740-750.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15632074 Free PMC article.
-
SMC protein complexes and the maintenance of chromosome integrity.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003;274:79-112. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-55747-7_4. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12596905 Review.
-
The SMC proteins and the coming of age of the chromosome scaffold hypothesis.Bioessays. 1995 Sep;17(9):759-66. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170905. Bioessays. 1995. PMID: 8763828 Review.
Cited by
-
BiFCo: visualizing cohesin assembly/disassembly cycle in living cells.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 May 9;6(7):e202301945. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202301945. Print 2023 Jul. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37160310 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes protein 1: Role in Genome Stability and Tumorigenesis.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Sep 3;13(8):1092-1099. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.21206. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28924389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Localization of human SMC1 protein at kinetochores.Chromosome Res. 2002;10(4):267-77. doi: 10.1023/a:1016563523208. Chromosome Res. 2002. PMID: 12199140
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae CTF18 and CTF4 are required for sister chromatid cohesion.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 May;21(9):3144-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.3144-3158.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11287619 Free PMC article.
-
A kinase-anchoring protein (AKAP)95 recruits human chromosome-associated protein (hCAP)-D2/Eg7 for chromosome condensation in mitotic extract.J Cell Biol. 2000 May 1;149(3):531-6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.3.531. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10791967 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

