Noncytopathic Sindbis virus RNA vectors for heterologous gene expression
- PMID: 9789028
- PMCID: PMC23682
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.12989
Noncytopathic Sindbis virus RNA vectors for heterologous gene expression
Abstract
Infection of vertebrate cells with alphaviruses normally leads to prodigious expression of virus-encoded genes and a dramatic inhibition of host protein synthesis. Recombinant Sindbis viruses and replicons have been useful as vectors for high level foreign gene expression, but the cytopathic effects of viral replication have limited their use to transient studies. We recently selected Sindbis replicons capable of persistent, noncytopathic growth in BHK cells and describe here a new generation of Sindbis vectors useful for long-term foreign gene expression based on such replicons. Foreign genes of interest as well as the dominant selectable marker puromycin N-acteyltransferase, which confers resistance to the drug puromycin, were expressed as subgenomic transcripts of noncytopathic replicons or defective-interfering genomes complemented in trans by a replicon. Based on these strategies, we developed vectors that can be initiated via either RNA or DNA transfection and analyzed them for their level and stability of foreign gene expression. Noncytopathic Sindbis vectors express reasonably high levels of protein in nearly every cell. These vectors should prove to be flexible tools for the rapid expression of heterologous genes under conditions in which cellular metabolism is not perturbed, and we illustrate their utility with a number of foreign proteins.
Figures
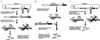

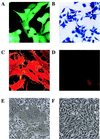
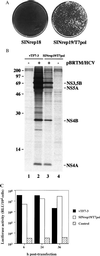
Comment in
-
RNA virus vectors: where are we and where do we need to go?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Oct 27;95(22):12750-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.12750. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9788984 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Strauss E G, Rice C M, Strauss J H. Virology. 1984;133:92–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

