Fluoroquinolone action against mycobacteria: effects of C-8 substituents on growth, survival, and resistance
- PMID: 9797236
- PMCID: PMC105976
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.11.2978
Fluoroquinolone action against mycobacteria: effects of C-8 substituents on growth, survival, and resistance
Abstract
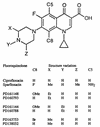
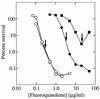
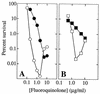
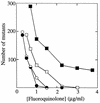
Fluoroquinolones trap gyrase on DNA as bacteriostatic complexes from which lethal DNA breaks are released. Substituents at the C-8 position increase activities of N-1-cyclopropyl fluoroquinolones against several bacterial species. In the present study, a C-8-methoxyl group improved bacteriostatic action against gyrA (gyrase-resistant) strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and M. bovis BCG. It also enhanced lethal action against gyrase mutants of M. bovis BCG. When cultures of M. smegmatis, M. bovis BCG, and M. tuberculosis were challenged with a C-8-methoxyl fluoroquinolone, no resistant mutant was recovered under conditions in which more than 1, 000 mutants were obtained with a C-8-H control. A C-8-bromo substituent also increased bacteriostatic and lethal activities against a gyrA mutant of M. bovis BCG. When lethal activity was normalized to bacteriostatic activity, the C-8-methoxyl compound was more bactericidal than its C-8-H control, while the C-8-bromo fluoroquinolone was not. The C-8-methoxyl compound was also found to be more effective than the C-8-bromo fluoroquinolone at reducing selection of resistant mutants when each was compared to a C-8-H control over a broad concentration range. These data indicate that a C-8-methoxyl substituent, which facilitates attack of first-step gyrase mutants, may help make fluoroquinolones effective antituberculosis agents.
Figures

References
-
- Agerton T, Valway S, Gore B, Pozsik C, Plikaytis B, Woodley C, Onorato I. Transmission of a highly drug-resistant strain (strain W1) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. JAMA. 1997;278:1073–1077. - PubMed
-
- Alangaden G J, Lerner S A. The clinical use of fluoroquinolones for the treatment of mycobacterial diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25:1213–1221. - PubMed
-
- Barnes P F, Bloch A B, Davidson P T, Snider D E. Tuberculosis in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1644–1650. - PubMed
-
- Bifani P, Plikaytis B B, Kapur V, Stockbauer K, Pan X, Lusfty M, Moghazeh S, Eisner W, Daniel T, Kaplan M, Crawford J T, Musser J M, Kreiswirth B N. Origin and interstate spread of a New York City multidrug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis clone family: adverse implications for tuberculosis control in the 21st century. JAMA. 1996;275:452–457. - PubMed
-
- Bloom B, Murray C. Tuberculosis: commentary on a reemergent killer. Science. 1992;251:1055–1064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

