Molecular characterization of plasmid-mediated oxytetracycline resistance in Aeromonas salmonicida
- PMID: 9797265
- PMCID: PMC106627
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.64.11.4194-4201.1998
Molecular characterization of plasmid-mediated oxytetracycline resistance in Aeromonas salmonicida
Abstract
Using broth conjugation, we found that 19 of 29 (66%) oxytetracycline (OT)-resistant isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida transferred the OT resistance phenotype to Escherichia coli. The OT resistance phenotype was encoded by high-molecular-weight R-plasmids that were capable of transferring OT resistance to both environmental and clinical isolates of Aeromonas spp. The molecular basis for antibiotic resistance in OT-resistant isolates of A. salmonicida was determined. The OT resistance determinant from one plasmid (pASOT) of A. salmonicida was cloned and used in Southern blotting and hybridization experiments as a probe. The determinant was identified on a 5.4-kb EcoRI fragment on R-plasmids from the 19 OT-resistant isolates of A. salmonicida. Hybridization with plasmids encoding the five classes (classes A to E) of OT resistance determinants demonstrated that the OT resistance plasmids of the 19 A. salmonicida isolates carried the class A resistance determinant. Analysis of data generated from restriction enzyme digests showed that the OT resistance plasmids were not identical; three profiles were characterized, two of which showed a high degree of homology.
Figures

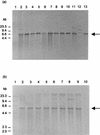
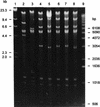
References
-
- Aoki T, Kitao T, Iemura N, Mitoma Y, Nomura T. The susceptibility of Aeromonas salmonicida strains isolated in cultured and wild salmonids to various chemotherapeutants. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish. 1983;49:17–22.
-
- Austin B, Austin D A. Bacterial fish pathogens: disease in farmed and wild fish. 2nd ed. Chichester, United Kingdom: Ellis Horwood; 1993.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

