Evaluation of lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides of different epitopic structures in the indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of brucellosis in small ruminants and cattle
- PMID: 9801329
- PMCID: PMC96196
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.6.749-754.1998
Evaluation of lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides of different epitopic structures in the indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of brucellosis in small ruminants and cattle
Abstract
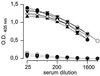
Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis have surface lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides carrying B. melitensis-type (M) and B. abortus-type (A) epitopes as well as common (C) epitopes present in all smooth Brucella biotypes. Crude lipopolysaccharides, hydrolytic O polysaccharides, and native hapten polysaccharides of MC or AC specificity were evaluated in indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays with polyclonal, monoclonal, or protein G conjugates by using sera from cattle, sheep, and goats infected with AC, MC, or AMC Brucella biotypes. Regardless of the antigen, the levels of antibodies were lower in goats than in sheep and highest in cattle. The diagnostic performance of the assay was not affected by the absence of lipid A-core epitopes, the presence of contaminating outer membrane proteins, the AC or MC epitopic structure of the absorbed antigen, or the conjugate used. Moreover, with sera from cattle vaccinated with B. abortus S19 (AC) or from sheep and goats vaccinated with B. melitensis Rev 1 (MC), AC and MC antigens showed similar levels of reactivity. The results show that antibodies to the C epitopes largely dominate in infection, and this is consistent with the existence of multiple overlapping C epitopes (V. Weynants, D. Gilson, A. Cloeckaert, A. Tibor, P. A. Denoel, F. Godfroid, J. N. Limet, and J.-J. Letesson, Infect. Immun. 65:1939-1943, 1997) rather than with one or two C epitopes. It is concluded that, by adaptation to the corresponding antibody levels, brucellosis in cattle, sheep, and goats can be diagnosed by immunosorbent assay with a single combination of conjugate and antigen.
Figures


References
-
- Abalos P, Pinochet L, Fábrega F. Prueba de ELISA para descartar la respuesta post-vacunal a Brucella abortus cepa 19. Av Cien Vet. 1993;8:138–143.
-
- Alonso-Urmeneta, B., C. Marín, J. M. Blasco, R. Díaz, and I. Moriyón. Unpublished data.
-
- Alton G G. Standardisation of agglutinating antigens for the diagnosis of brucellosis. Res Vet Sci. 1971;12:330–337. - PubMed
-
- Alton G G, Jones L M, Angus R D, Verger J M. Techniques for the brucellosis laboratory. Paris, France: Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique; 1988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

