Levels of cytokines and immune activation markers in plasma in human immunodeficiency virus infection: quality control procedures
- PMID: 9801330
- PMCID: PMC96197
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.6.755-761.1998
Levels of cytokines and immune activation markers in plasma in human immunodeficiency virus infection: quality control procedures
Abstract
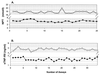
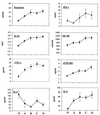
Procedures for quality control (QC) in a laboratory that concentrates on cytokine and soluble marker measurements in biological fluids are outlined. Intra-assay, interassay, and interlaboratory experiences are presented. Plasma and serum beta2-microglobulin (beta2M) and neopterin test data are presented in greatest detail, along with substantial tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), gamma interferon, soluble interleukin-2 receptor-alpha (sIL-2Ralpha), sTNF-RII, IL-4, and IL-6 data. Recommended QC procedures for cytokine and soluble-marker testing include replicate testing of two or more reference samples provided by the kit manufacturer, replicate testing of in-house frozen reference QC samples that represent normal and abnormal analyte contents, retesting 15 to 20% of randomly selected samples, and comparing normal reference ranges each year. Also, eight cytokines and soluble markers were evaluated in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-seronegative and HIV-seropositive individuals stratified on the basis of CD4 T-cell numbers. Levels of some but not all cytokines in serum increased in HIV infection. There was a tendency for cytokines to increase with more advanced disease, defined by reduced CD4 T-cell numbers. Cytokine changes did not relate closely to CD4 level, indicating that separate information was provided by the measurements of TNF-alpha, sTNF-RII, sIL-2Ralpha, beta2M, and neopterin. Serum IL-4 and TNF-alpha levels were not increased. The quality of laboratory data can impact on clinical relevance. Interlaboratory comparisons revealed substantial differences at some sites and documented the need for external proficiency-testing quality assurance programs.
Figures

References
-
- Aggarwal B B, Puri R K. Common and uncommon features of cytokines and cytokine receptors: an overview. In: Aggarwal B B, Puri R K, editors. Human cytokines: their role in disease and therapy. Cambridge, Mass: Blackwell Science; 1995. pp. 3–24.
-
- Aukrust P, Liabakk N B, Müller F, Lien E, Espevik T, Froland S S. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and soluble TNF receptors in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: correlations to clinical immunologic and virologic parameters. J Infect Dis. 1994;169:420–424. - PubMed
-
- Bass H Z, Nishanian P, Hardy W D, Mitsuyasu R T, Esmail E, Cumberland W, Fahey J L. Immune changes in HIV infection: significant correlations and differences in serum markers and lymphoid phenotypic antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1992;64:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Bienvenu J, Coulon L, Doche C, Gutowski M C, Grau G. Analytical performances of commercial ELISA kits for IL-2, IL-6 and TNFα. A WHO study. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1993;4:447–451. - PubMed
-
- Cannon J G, Nerad J L, Poutsiaka D D, Dinarello C A. Measuring circulating cytokines. J Appl Physiol. 1993;75:1897–1902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

