kappa-opioid regulation of neuronal activity in the rat supraoptic nucleus in vivo
- PMID: 9801385
- PMCID: PMC6792869
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-22-09480.1998
kappa-opioid regulation of neuronal activity in the rat supraoptic nucleus in vivo
Abstract
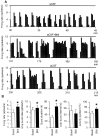
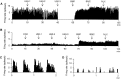
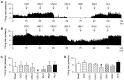
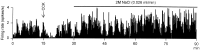
We investigated the influence of endogenous kappa-opioids on the activity of supraoptic neurons in vivo. Administration of the kappa-antagonist nor-binaltorphimine (200 micrograms/kg, i.v.), increased the activity of phasic (vasopressin), but not continuously active (oxytocin), supraoptic neurons by increasing burst duration (by 69 +/- 24%) and decreasing the interburst interval (by 19 +/- 11%). Similarly, retrodialysis of nor-binaltorphimine onto the supraoptic nucleus increased the burst duration (119 +/- 57% increase) of vasopressin cells but did not alter the firing rate of oxytocin cells (4 +/- 8% decrease). Thus, an endogenous kappa-agonist modulates vasopressin cell activity by an action within the supraoptic nucleus. To eliminate kappa-agonist actions within the supraoptic nucleus, we infused the kappa-agonist U50,488H (2.5 micrograms/hr at 0.5 micrograms/hr) into one supraoptic nucleus over 5 d to locally downregulate kappa-receptor function. Such infusions reduced the spontaneous activity of vasopressin but not oxytocin cells and reduced the proportion of cells displaying spontaneous phasic activity from 26% in vehicle-infused nuclei to 3% in U50, 488H-infused nuclei; this treatment also prevented acute inhibition of both vasopressin and oxytocin cells by U50,488H (1000 micrograms/kg, i.v.), confirming functional kappa-receptor downregulation. In U50, 488H-infused supraoptic nuclei, vasopressin cell firing rate was increased by nor-binaltorphimine (100 and 200 micrograms/kg, i.v.) but not to beyond that found in vehicle-treated nuclei, indicating that these cells were not U50,488H-dependent. Thus, normally functioning kappa-opioid mechanisms on vasopressin cells are essential for the expression of phasic firing.
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong WE, Scholer J, McNeill TH. Immunocytochemical, Golgi and electron microscopic characterization of putative dendrites in the ventral glial lamina of the rat supraoptic nucleus. Neuroscience. 1982;7:679–694. - PubMed
-
- Bicknell RJ, Chapman C, Leng G. Effects of opioid agonists and antagonists on oxytocin and vasopressin release in vitro. Neuroendocrinology. 1985;41:142–148. - PubMed
-
- Bondy CA, Gainer H, Russell JT. Dynorphin A inhibits and naloxone increases the electrically stimulated release of oxytocin but not vasopressin from the terminals of the neural lobe. Endocrinology. 1988;122:1321–1327. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
