Stealth ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ release contributes to activity of capacitative Ca2+ entry and nitric oxide synthase in bovine endothelial cells
- PMID: 9806989
- PMCID: PMC2231284
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.369bb.x
Stealth ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ release contributes to activity of capacitative Ca2+ entry and nitric oxide synthase in bovine endothelial cells
Abstract
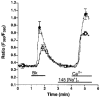
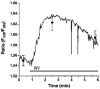
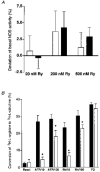
1. The involvement of ryanodine-sensitive Ca2+ release (RsCR) in bradykinin (Bk)-induced Ca2+ release, capacitative Ca2+ entry (CCE) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activation was assessed in freshly isolated bovine coronary artery endothelial cells. 2. Using deconvolution microscopy fura-2 was found throughout the whole cytosol, while the cell membrane impermeable dye FFP-18 was exclusively in the cell membrane. Thus, perinuclear ([Ca2+]pn) and subplasmalemmal Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]sp) were monitored using fura-2 and FFP-18. 3. Inhibition of Na+-Ca2+ exchange by lowering extracellular Na+ concentration augmented the Bk-induced [Ca2+]pn signal in Ca2+-free solution. This effect was abolished when RsCR was prevented with 25 micromol l-1 ryanodine, while inhibition of RsCR had no effect on Bk-induced increase in [Ca2+]pn without inhibition of Na+-Ca2+ exchange. 4. Initiating RsCR by 200 nmol l-1 ryanodine increased [Ca2+]sp, while [Ca2+]pn remained constant. However, when Na+-Ca2+ exchange was prevented, ryanodine was also able to elevate [Ca2+]pn. 5. Blockage of RsCR diminished Ca2+ extrusion in response to stimulation with Bk in normal Na+-containing solution. 6. Inhibition of RsCR blunted Bk-activated CCE, while inhibition of Na+-Ca2+ exchange during stimulation enhanced CCE. 7. Although direct activation of RsCR failed to activate NOS, inhibition of RsCR diminished the effect of ATP and Bk on NOS, while the effect of thapsigargin remained unchanged. 8. These data suggest that during stimulation subplasmalemmal RsCR occurs, which contributes to the activities of CCE and NOS. Thus, the function of the subplasmalemmal Ca2+ control unit must be extended as a regulator for CCE and NOS.
Figures






References
-
- Busse R, Fichter H, Lückhoff A, Kohlhardt M. Hyperpolarization and increased free calcium in acetylcholine-stimulated endothelial cell. American Journal of Physiology. 1988;255:H965–969. - PubMed
-
- Colden-Stanfield M, Schilling WP, Ritchie AK, Eskin SG, Navarro LT, Kunze DL. Bradykinin-induced increases in cytosolic free calcium and ionic currents in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Circulation Research. 1987;61:632–640. - PubMed
-
- Corda S, Spurgeon HA, Lakatta EG, Capogrossi MC, Ziegelstein R. Endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ depletion unmasks a caffeine-induced Ca2+ influx in human aortic endothelial cells. Circulation Research. 1995;77:927–935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

