A novel nuclear member of the thioredoxin superfamily
- PMID: 9808743
- PMCID: PMC34809
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.118.3.987
A novel nuclear member of the thioredoxin superfamily
Abstract
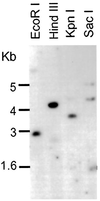
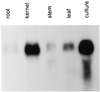
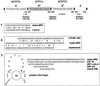
We describe the isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding maize (Zea mays L.) nucleoredoxin (NRX), a novel nuclear protein that is a member of the thioredoxin (TRX) superfamily. NRX is composed of three TRX-like modules arranged as direct repeats of the classic TRX domain. The first and third modules contain the amino acid sequence WCPPC, which indicates the potential for TRX oxidoreductase activity, and insulin reduction assays indicate that at least the third module possesses TRX enzymatic activity. The carboxy terminus of NRX is a non-TRX module that possesses C residues in the proper sequence context to form a Zn finger. Immunolocalization preferentially to the nucleus within developing maize kernels suggests a potential for directed alteration of the reduction state of transcription factors as part of the events and pathways that regulate gene transcription.
Figures






References
-
- Buchanan BB, Schurmann P, Decottignies P, Lozano RM. Thioredoxin: a multifunctional regulatory protein with a bright future in technology and medicine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;314:257–260. - PubMed
-
- Darby NJ, Kemmink J, Creighton TE. Identifying and characterizing a structural domain of protein disulfide isomerase. Biochemistry. 1996;35:10517–10528. - PubMed
-
- Eklund H, Gleason FK, Holmgren A. Structural and functional relations among thioredoxins of different species. Proteins. 1991;11:13–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

