Tau pathology in two Dutch families with mutations in the microtubule-binding region of tau
- PMID: 9811325
- PMCID: PMC1853390
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65721-5
Tau pathology in two Dutch families with mutations in the microtubule-binding region of tau
Abstract
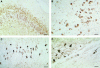
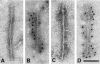
Different mutations in the microtubule-associated tau protein gene have recently been identified in several families with hereditary frontotemporal dementia and Parkinsonism (FTDP-17) linked to chromosome 17q21-22. Some families show neuronal and glial deposits containing hyperphosphorylated tau in several brain regions. We have investigated the presence of tau deposits by using a panel of anti-tau antibodies in three brains of a family with the P301L mutation (HFTD1) and in another family with the G272V mutation (HFTD2) of the tau gene. Numerous intracytoplasmic tau deposits in neurons, glial cells, and neurites were found in hippocampal formation, neocortex, and substantia nigra. These deposits in three patients from HFTD1 consisted of slender twisted filaments 15 nm wide with variable periodicity and a few straight filaments. Tau extracted from these filaments appeared as two major bands of 64 and 68 kd and a minor band of 72 kd that, after alkaline phosphatase treatment, proved to consist mainly of 4-repeat tau isoforms and one of the 3-repeat isoforms. In three patients from HFTD2 numerous Pick-like bodies were present. The conclusion is that the type and distribution of tau deposits in HFTD1 and HFTD2, the physical structure of filaments, and tau isoform composition in HFTD1 differ from Alzheimer's disease and an FTDP-17 family with a V337M mutation in the tau gene.
Figures

References
-
- Foster NL, Wilhelmsen K, Sima AAF, Jones MZ, D’Amato C, Gilman S, Spillantini MG, Lynch T, Mayeux RP, Gaskell Ph-C, Hulette C, Pericak-Vance MA, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Dickson DW, Heutink P, Kros J, van Swieten JC, Arwert F, Ghetti B, Murrell J, Lannfelt L, Hutton M, Phelps CH, Snyder DS, Oliver E, Ball MJ, Cummings JL, Miller BL, Katzman R, Reed L, Schelper RL, Lanska DJ, Brun A, Fink JK, Khul DE, Knopman DS, Wszolek Z, Miller CL, Bird TD, Lendon C, Elechi C: Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17: a consensus statement. Ann Neurol 1997, 41:706-715 - PubMed
-
- Sima AAF, Defendini R, Keohane C, D’Amato C, Foster NL, Parchi P, Gambetti M, Lynch T, Wilhelmsen KC: The neuropathology of chromosome 17-linked dementia. Ann Neurol 1996, 39:734-743 - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Goedert M: Comparison of the neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease and familial presenile dementia with tangles. Acta Neuropathol 1996, 92:42-48 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

