CD4(+) T cells prevent spontaneous experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in anti-myelin basic protein T cell receptor transgenic mice
- PMID: 9815265
- PMCID: PMC2212404
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1875
CD4(+) T cells prevent spontaneous experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in anti-myelin basic protein T cell receptor transgenic mice
Abstract
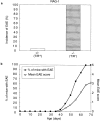
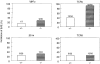
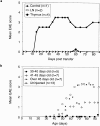
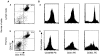
Autoimmune diseases result from a failure of tolerance. Although many self-reactive T cells are present in animals and humans, their activation appears to be prevented normally by regulatory T cells. In this study, we show that regulatory CD4(+) T cells do protect mice against the spontaneous occurrence of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a mouse model for multiple sclerosis. Anti-myelin basic protein (MBP) TCR transgenic mice (T/R+) do not spontaneously develop EAE although many self-reactive T cells are present in their thymi and peripheral lymphoid organs. However, the disease develops in all crosses of T/R+ mice with recombination-activating gene (RAG)-1 knockout mice in which transgenic TCR-expressing cells are the only lymphocytes present (T/R- mice). In this study, crosses of T/R+ mice with mice deficient for B cells, CD8(+) T cells, NK1.1 CD4(+) T (NKT) cells, gamma/delta T cells, or alpha/beta T cells indicated that alpha/beta CD4(+) T cells were the only cell population capable of controlling the self-reactive T cells. To confirm the protective role of CD4(+) T cells, we performed adoptive transfer experiments. CD4(+) T cells purified from thymi or lymph nodes of normal mice prevented the occurrence of spontaneous EAE in T/R- mice. To achieve full protection, the cells had to be transferred before the recipient mice manifested any symptoms of the disease. Transfer of CD4(+) T cells after the appearance of symptoms of EAE had no protective effect. These results indicate that at least some CD4(+) T cells have a regulatory function that prevent the activation of self-reactive T cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory CD4(+) T cells expressing endogenous T cell receptor chains protect myelin basic protein-specific transgenic mice from spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Exp Med. 1998 Nov 16;188(10):1883-94. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1883. J Exp Med. 1998. PMID: 9815266 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous CD4+BV8S2- T cells from TG BV8S2+ donors confer complete protection against spontaneous experimental encephalomyelitis (Sp-EAE) in TCR transgenic, RAG-/- mice.J Neurosci Res. 2003 Jan 1;71(1):89-103. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10450. J Neurosci Res. 2003. PMID: 12478617
-
Repertoire requirements of CD4+ T cells that prevent spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2000 May 15;164(10):5499-507. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.10.5499. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10799918
-
Regulatory T cells in spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Immunol Rev. 2001 Aug;182:122-34. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1820110.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11722629 Review.
-
Tolerance and autoimmunity in TCR transgenic mice specific for myelin basic protein.Immunol Rev. 1999 Jun;169(1):147-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01313.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10450515 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rebuilding an immune-mediated central nervous system disease: weighing the pathogenicity of antigen-specific versus bystander T cells.J Immunol. 2004 Oct 15;173(8):4779-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.8.4779. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15470017 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated view of suppressor T cell subsets in immunoregulation.J Clin Invest. 2004 Nov;114(9):1198-208. doi: 10.1172/JCI23411. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15520848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Normal regulatory alpha/beta T cells effectively eliminate abnormally activated T cells lacking the interleukin 2 receptor beta in vivo.J Exp Med. 1999 Dec 6;190(11):1561-72. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.11.1561. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10587347 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired development of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in the absence of STAT1: increased susceptibility to autoimmune disease.J Exp Med. 2004 Jan 5;199(1):25-34. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020509. Epub 2003 Dec 29. J Exp Med. 2004. PMID: 14699080 Free PMC article.
-
Immune tolerance to myelin proteins.Immunol Res. 2003;28(3):201-21. doi: 10.1385/IR:28:3:201. Immunol Res. 2003. PMID: 14713715 Review.
References
-
- Kappler JW, Roehm N, Marrack P. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 1987;49:273–280. - PubMed
-
- Hammerling GJ, Schonrich G, Ferber I, Arnold B. Peripheral tolerance as a multi-step mechanism. Immunol Rev. 1993;133:93–104. - PubMed
-
- Rocha B, von Boehmer H. Peripheral selection of the T cell repertoire. Science. 1991;251:1225–1228. - PubMed
-
- Gleeson PA, Toh BH, van Driel IR. Organ-specific autoimmunity induced by lymphopenia. Immunol Rev. 1996;149:97–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

