The high osmolarity glycerol response (HOG) MAP kinase pathway controls localization of a yeast golgi glycosyltransferase
- PMID: 9817752
- PMCID: PMC2132948
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.143.4.935
The high osmolarity glycerol response (HOG) MAP kinase pathway controls localization of a yeast golgi glycosyltransferase
Abstract
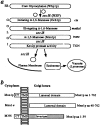
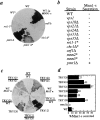
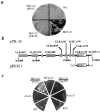
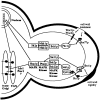
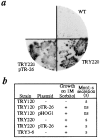
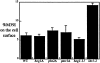
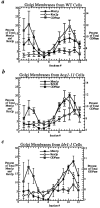
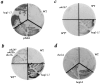
The yeast alpha-1,3-mannosyltransferase (Mnn1p) is localized to the Golgi by independent transmembrane and lumenal domain signals. The lumenal domain is localized to the Golgi complex when expressed as a soluble form (Mnn1-s) by exchange of its transmembrane domain for a cleavable signal sequence (Graham, T. R., and V. A. Krasnov. 1995. Mol. Biol. Cell. 6:809-824). Mutants that failed to retain the lumenal domain in the Golgi complex, called lumenal domain retention (ldr) mutants, were isolated by screening mutagenized yeast colonies for those that secreted Mnn1-s. Two genes were identified by this screen, HOG1, a gene encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) that functions in the high osmolarity glycerol (HOG) pathway, and LDR1. We have found that basal signaling through the HOG pathway is required to localize Mnn1-s to the Golgi in standard osmotic conditions. Mutations in HOG1 and LDR1 also perturb localization of intact Mnn1p, resulting in its loss from early Golgi compartments and a concomitant increase of Mnn1p in later Golgi compartments.
Figures
References
-
- Acharya U, Mallabiabarrena A, Acharya JK, Malhotra V. Signaling via mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK1) is required for Golgi fragmentation during mitosis. Cell. 1998;92:183–192. - PubMed
-
- Brewster JL, de Valoir T, Dwyer ND, Winter E, Gustin MC. An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in yeast. Science. 1993;259:1760–1763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

