Genetic variability among group A and group B respiratory syncytial viruses in a children's hospital
- PMID: 9817872
- PMCID: PMC105239
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.12.3552-3557.1998
Genetic variability among group A and group B respiratory syncytial viruses in a children's hospital
Abstract
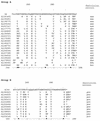
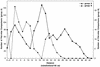
Respiratory syncytial (RS) viruses isolated over three epidemic periods in a children's hospital in the United States were analyzed. The viruses (n = 174) were characterized as to major antigenic group (group A or B) by a PCR-based assay. Group A RS viruses were dominant the first 2 years, followed by a year with group B dominance (ratios of group A to group B viruses for epidemic periods, 56/4 for 1993-1994, 42/3 for 1994-1995, and 19/50 for 1995-1996). Genetic variability within the groups was assessed by restriction fragment analysis of PCR products; 79 isolates were also analyzed by nucleotide sequence determination of a variable region of the glycoprotein G gene. Among the group A RS virus isolates, this G-protein variable region had amino acid differences of as great as 38%. The G-protein amino acids of the group A viruses differed by up to 31% from the G-protein amino acids of a prototype (A2) group A virus. Among the group B RS virus G proteins, amino acid differences were as great as 14%. The G-protein amino acids of the group B viruses differed by up to 27% from the G-protein amino acids of a prototype (18537) group B virus. The group A and group B RS viruses demonstrated genetic variability between years and within individual years. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that there were multiple evolutionary lineages among both the group A and group B viruses. Among the recent group B isolates, variability was less than that seen for the group A viruses. However, comparisons to prototype strains revealed that the group B RS viruses may vary more extensively than was observed over the 3 years studied in the present investigation.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson L J, Hendry R M, Pierik L T, Tsou C, McIntosh K. Multicenter study of strains of respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis. 1991;163:687–692. - PubMed
-
- Anderson L J, Hierholzer J C, Tsou C, Hendry R M, Fernie B F, Stone Y, McIntosh K. Antigenic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus strains with monoclonal antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:626–633. - PubMed
-
- Cane P A. Analysis of linear epitopes recognised by the primary human antibody response to a variable region of the attachment (G) protein of respiratory syncytial virus. J Med Virol. 1997;51:297–304. - PubMed
-
- Cane P A, Matthews D A, Pringle C R. Identification of variable domains of the attachment (G) protein of subgroup A respiratory syncytial viruses. J Gen Virol. 1991;72:2091–2096. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

