Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase of large-cell anaplastic lymphoma is a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that utilizes phospholipase C-gamma to mediate its mitogenicity
- PMID: 9819383
- PMCID: PMC109278
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.12.6951
Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase of large-cell anaplastic lymphoma is a constitutively active tyrosine kinase that utilizes phospholipase C-gamma to mediate its mitogenicity
Abstract
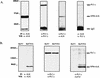
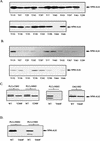
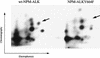
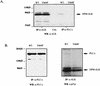
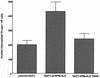
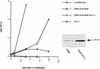
Large-cell anaplastic lymphoma is a subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma characterized by the expression of CD30. More than half of these lymphomas have a chromosomal translocation, t(2;5), that leads to the expression of a hybrid protein comprised of the nucleolar phosphoprotein nucleophosmin (NPM) and the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). Here we show that transfection of the constitutively active tyrosine kinase NPM-ALK into Ba/F3 and Rat-1 cells leads to a transformed phenotype. Oncogenic tyrosine kinases transform cells by activating the mitogenic signal transduction pathways, e.g., by binding and activating SH2-containing signaling molecules. We found that NPM-ALK binds most specifically to the SH2 domains of phospholipase C-gamma (PLC-gamma) in vitro. Furthermore, we showed complex formation of NPM-ALK and PLC-gamma in vivo by coimmunoprecipitation experiments in large-cell anaplastic lymphoma cells. This complex formation leads to the tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of PLC-gamma, which can be corroborated by enhanced production of inositol phosphates (IPs) in NPM-ALK-expressing cells. By phosphopeptide competition experiments, we were able to identify the tyrosine residue on NPM-ALK responsible for interaction with PLC-gamma as Y664. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we constructed a comprehensive panel of tyrosine-to-phenylalanine NPM-ALK mutants, including NPM-ALK(Y664F). NPM-ALK(Y664F), when transfected into Ba/F3 cells, no longer forms complexes with PLC-gamma or leads to PLC-gamma phosphorylation and activation, as confirmed by low IP levels in these cells. Most interestingly, Ba/F3 and Rat-1 cells expressing NPM-ALK(Y664F) also show a biological phenotype in that they are not stably transformed. Overexpression of PLC-gamma can partially rescue the proliferative response of Ba/F3 cells to the NPM-ALK(Y664F) mutant. Thus, PLC-gamma is an important downstream target of NPM-ALK that contributes to its mitogenic activity and is likely to be important in the molecular pathogenesis of large-cell anaplastic lymphomas.
Figures
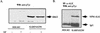




References
-
- Alimandi M, Heidaran M A, Gutkind J S, Zhang J, Ellmore N, Valius M, Kazlauskas A, Pierce J H, Li W. PLC-gamma activation is required for PDGF-betaR-mediated mitogenesis and monocytic differentiation of myeloid progenitor cells. Oncogene. 1997;15:585–593. - PubMed
-
- Atherton E, Sheppard R C. Solid phase peptide synthesis—a practical approach. Oxford, England: IRL Press; 1989.
-
- Bartram C R, de Klein A, Hagemeijer A, van Agthoven T, van Kessel A D, Bootsma D, Grosveld G, Ferguson-Smith M A, Davies T, Stone M, Heisterkamp N, Stephenson J R, Groffen J. Translocation of c-Abl oncogene correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukemia. Nature. 1983;306:277–280. - PubMed
-
- Borer R A, Lehner C F, Eppenberger H M, Nigg E A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989;56:379–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
