The lymnaea cardioexcitatory peptide (LyCEP) receptor: a G-protein-coupled receptor for a novel member of the RFamide neuropeptide family
- PMID: 9822740
- PMCID: PMC6793288
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-23-09812.1998
The lymnaea cardioexcitatory peptide (LyCEP) receptor: a G-protein-coupled receptor for a novel member of the RFamide neuropeptide family
Abstract
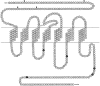
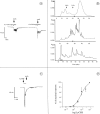
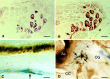
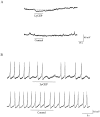
A novel G-protein-coupled receptor (GRL106) resembling neuropeptide Y and tachykinin receptors was cloned from the mollusc Lymnaea stagnalis. Application of a peptide extract from the Lymnaea brain to Xenopus oocytes expressing GRL106 activated a calcium-dependent chloride channel. Using this response as a bioassay, we purified the ligand for GRL106, Lymnaea cardioexcitatory peptide (LyCEP), an RFamide-type decapeptide (TPHWRPQGRF-NH2) displaying significant similarity to the Achatina cardioexcitatory peptide (ACEP-1) as well as to the recently identified family of mammalian prolactin-releasing peptides. In the Lymnaea brain, the cells that produce egg-laying hormone are the predominant site of GRL106 gene expression and appear to be innervated by LyCEP-containing fibers. Indeed, LyCEP application transiently hyperpolarizes isolated egg-laying hormone cells. In the Lymnaea pericardium, LyCEP-containing fibers end blindly at the pericardial lumen, and the heart is stimulated by LyCEP in vitro. These data confirm that LyCEP is an RFamide ligand for GRL106.
Figures


References
-
- Aloyz RS, DesGroseillers L. Processing of the L5–67 precursor peptide and characterization of LUQIN in the LUQ neurons of Aplysia californica. Peptides. 1995;16:331–338. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury AF, Smyth DG. Peptide amidation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991;16:112–115. - PubMed
-
- Brussaard AB, Kits KS, Ter Maat A, Van Minnen J, Moed PJ. Dual inhibitory action of FMRFamide on neurosecretory cells controlling egg laying behavior in the pond snail. Brain Res. 1988;447:35–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
