The murine gene p27Kip1 is haplo-insufficient for tumour suppression
- PMID: 9823898
- PMCID: PMC5395202
- DOI: 10.1038/24179
The murine gene p27Kip1 is haplo-insufficient for tumour suppression
Abstract
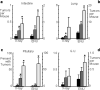
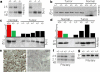
p27Kip is a candidate human tumour-suppressor protein, because it is able to inhibit cyclin-dependent kinases and block cell proliferation. Abnormally low levels of the p27 protein are frequently found in human carcinomas, and these low levels correlate directly with both histological aggressiveness and patient mortality. However, it has not been possible to establish a causal link between p27 and tumour suppression, because only rare instances of homozygous inactivating mutations of the p27 gene have been found in human tumours. Thus, p27Kip1 does not fulfil Knudson's 'two-mutation' criterion for a tumour-suppressor gene. Here we show that both p27 nullizygous and p27 heterozygous mice are predisposed to tumours in multiple tissues when challenged with gamma-irradiation or a chemical carcinogen. Therefore p27 is a multiple-tissue tumour suppressor in mice. Molecular analyses of tumours in p27 heterozygous mice show that the remaining wild-type allele is neither mutated nor silenced. Hence, p27 is haplo-insufficient for tumour suppression. The assumption that null mutations in tumour-suppressor genes are recessive excludes those genes that exhibit haplo-insufficiency.
Figures
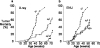
References
-
- Polyak K, et al. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994;8:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Nourse J, et al. Interleukin-2-mediated elimination of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor prevented by rapamycin. Nature. 1994;372:570–573. - PubMed
-
- Kato JY, Matsuoka M, Polyak K, Massague J, Sherr CJ. Cyclin AMP-induced G1 phase arrest mediated by an inhibitor (p27Kip1) of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 activation. Cell. 1994;79:487–496. - PubMed
-
- Coats S, Flanagan WM, Nourse J, Roberts JM. Requirement of p27Kip1 for restriction point control of the fibroblast cell cycle. Science. 1996;272:877–880. - PubMed
-
- Fero ML, et al. A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27Kip1-deficient mice. Cell. 1996;85:733–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

