Identification of immunodominant regions within the C-terminal cell binding domain of intimin alpha and intimin beta from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 9826337
- PMCID: PMC108713
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5643-5649.1998
Identification of immunodominant regions within the C-terminal cell binding domain of intimin alpha and intimin beta from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
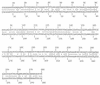
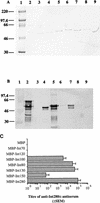
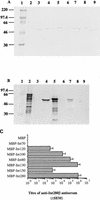
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) strains are a common cause of infantile diarrhea in developing countries. EPEC strains induce a characteristic attaching and effacing (A/E) lesion on epithelial cells. A/E lesion formation requires intimin, an outer membrane adhesin protein. The cell-binding activity of intimin is localized at the C-terminal 280 amino acids of the polypeptide (Int280). So far, four distinct Int280 types (alpha, beta, gamma, and delta) have been identified. The aim of this study was to identify immunodominant regions within the Int280alpha and Int280beta domains. Recombinant DNA was used to construct and express overlapping polypeptides spanning these domains. Rabbit anti-Int280 antisera and human colostral immunoglobulin A were reacted with these polypeptides in Western blots and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. The results obtained with the rabbit antisera showed the presence of two separate immunodominant regions which are common to both Int280alpha and Int280beta. The first localized within the N-terminal region of Int280, and the second localized between amino acids 80 and 130. The results with the human colostra revealed one reactivity pattern against the Int280alpha fragments but two different reactivity patterns against the Int280beta domain.
Figures



References
-
- Burnette W N. “Western blotting”: electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981;112:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Camara L M, Carbonare S B, Silva M L, Carneiro Sampaio M M. Inhibition of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) adhesion to HeLa cells by human colostrum: detection of specific IgA related to EPEC outer-membrane proteins. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1994;103:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Cantey J R, Blake R K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977;135:454–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

