TetR is a positive regulator of the tetanus toxin gene in Clostridium tetani and is homologous to botR
- PMID: 9826344
- PMCID: PMC108720
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5698-5702.1998
TetR is a positive regulator of the tetanus toxin gene in Clostridium tetani and is homologous to botR
Abstract
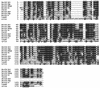
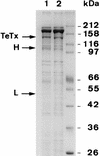
The TetR gene immediately upstream from the tetanus toxin (TeTx) gene was characterized. It encodes a 21,562-Da protein which is related (50 to 65% identity) to the equivalent genes (botR) in Clostridium botulinum. TetR has the feature of a DNA binding protein with a basic pI (9.53). It contains a helix-turn-helix motif and shows 29% identity with other putative regulatory genes in Clostridium, i.e., uviA from C. perfringens and txeR from C. difficile. We report for the first time the transformation of C. tetani by electroporation, which permitted us to investigate the function of tetR. Overexpression of tetR in C. tetani induced an increase in TeTx production and in the level of the corresponding mRNA. This indicates that TetR is a transcriptional activator of the TeTx gene. Overexpression of botR/A (60% identity with TetR at the amino acid level) in C. tetani induced an increase in TeTx production comparable to that for overexpression of tetR. However, botR/C (50% identity with TetR at the amino acid level) was less efficient. This supports that TetR positively regulates the TeTx gene in C. tetani and that a conserved mechanism of regulation of the neurotoxin genes is involved in C. tetani and C. botulinum.
Figures




References
-
- Bhandari M, Campbell K D, Collins M D, East A K. Molecular characterization of the clusters of genes encoding the botulinum neurotoxin complex in Clostridium botulinum (Clostridium argentinense) type G and nonproteolytic Clostridium botulinum type B. Curr Microbiol. 1997;35:207–214. - PubMed
-
- Burnette W N. Western-blotting: electrophoresis transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981;112:115–203. - PubMed
-
- Clare J J, Rayment F B, Ballantine S P, Sreekrishna K, Romanos M A. High-level expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in Pichia pastoris strains containing multiple tandem integrations of the gene. Bio/Technology. 1991;9:455–460. - PubMed
-
- East A K, Bhandari M, Stacey J M, Campbell K D, Collins M D. Organization and phylogenetic interrelationships of genes encoding components of the botulinum toxin complex in proteolytic Clostridium botulinum types A, B, and F: evidence of chimeric sequences in the gene encoding the nontoxic nonhemagglutinin component. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996;46:1105–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

