Cloning, expression, and sequencing of a cell surface antigen containing a leucine-rich repeat motif from Bacteroides forsythus ATCC 43037
- PMID: 9826345
- PMCID: PMC108721
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5703-5710.1998
Cloning, expression, and sequencing of a cell surface antigen containing a leucine-rich repeat motif from Bacteroides forsythus ATCC 43037
Abstract
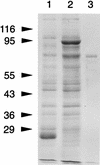
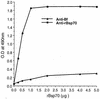
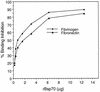
Bacteroides forsythus is a recently recognized human periodontopathogen associated with advanced, as well as recurrent, periodontitis. However, very little is known about the mechanism of pathogenesis of this organism. The present study was undertaken to identify the surface molecules of this bacterium that may play roles in its adherence to oral tissues or triggering of a host immune response(s). The gene (bspA) encoding a cell surface-associated protein of B. forsythus with an apparent molecular mass of 98 kDa was isolated by immunoscreening of a B. forsythus gene library constructed in a lambda ZAP II vector. The encoded 98-kDa protein (BspA) contains 14 complete repeats of 23 amino acid residues that show partial homology to leucine-rich repeat motifs. A recombinant protein containing the repeat region was expressed in Escherichia coli, purified, and utilized for antibody production, as well as in vitro binding studies. The purified recombinant protein bound strongly to fibronectin and fibrinogen in a dose-dependent manner and further inhibited the binding of B. forsythus cells to these extracellular matrix (ECM) components. In addition, adult patients with B. forsythus-associated periodontitis expressed specific antibodies against the BspA protein. We report here the cloning and expression of an immunogenic cell surface-associated protein (BspA) of B. forsythus and speculate that it mediates the binding of bacteria to ECM components and clotting factors (fibronectin and fibrinogen, respectively), which may be important in the colonization of the oral cavity by this bacterium and is also a target for the host immune response.
Figures




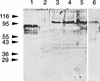
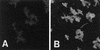
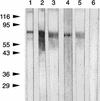
References
-
- Ausubel F A, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1996.
-
- Bakker D, Willemsen P T J, Simons L H, van Zijderveld F G, de Graff F K. Characterization of the antigenic and adhesive properties of FaeG, the major subunit of K88 fimbriae. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:247–255. - PubMed
-
- Grossi S G, Genco R J, Machtei E E, Ho A W, Koch G, Dunford R G, Zambon J, Hausmann E. Assessment of risk for periodontal disease. II. Risk indicators for alveolar bone loss. J Periodontol. 1995;66:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Grossi S G, Zambon J J, Ho A W, Koch G, Dunford R G, Machtei E E, Norderyd O M, Genco R J. Assessment of risk for periodontal disease. I. Risk indicators for attachment loss. J Periodontol. 1994;65:260–267. - PubMed
-
- Guillot E, Mouton C. A PCR-DNA based assay specific for Bacteroides forsythus. Mol Cell Probes. 1996;10:413–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

