Estimation of group B streptococcus type III polysaccharide-specific antibody concentrations in human sera is antigen dependent
- PMID: 9826364
- PMCID: PMC108740
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5848-5853.1998
Estimation of group B streptococcus type III polysaccharide-specific antibody concentrations in human sera is antigen dependent
Abstract
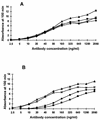
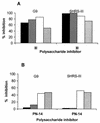
The presence of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against group B streptococcus (GBS) type III polysaccharide (PS) has been correlated with protection against GBS disease. The GBS type III PS is structurally similar to the pneumococcal type 14 PS, differing only in the presence of sialic acid residues. Four different preparations of GBS type III PS were evaluated for their specificity in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): free PS, free PS mixed with methylated human serum albumin (mHSA), PS conjugated to biotin and PS conjugated to human serum albumin. Three groups of human sera were used to evaluate these PS preparations: sera from recipients of a GBS PS vaccine, sera from women receiving a GBS type III PS-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccine, and sera from nonimmunized healthy women of childbearing age. Estimated antibody concentrations were different depending on the PS preparation used. Using any of the four preparations, we were able to measure </=0.05 micrograms of IgG antibody to the GBS type III PS per ml. The specificity of the assay was determined by competitive inhibition with homologous and heterologous PS. The pneumococcal type 14 PS did not inhibit binding of antibody to the native GBS type III PS in sera from adults receiving the GBS PS vaccine or in sera from nonimmunized adults (except serum G9). The pneumococcal type 14 PS inhibited 50% in sera from recipients of GBS type III conjugate vaccine and in serum G9 when GBS type III PS conjugated to biotin or to HSA was used as antigen in ELISA. These data show that free GBS type III PS or PS mixed with mHSA is a sensitive and specific antigen for ELISA and that conjugation can alter the antigenic specificity of a PS.
Figures



References
-
- Anthony B F, Concepcion N F, Concepcion K F. Human antibody to the group-specific polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:221–226. - PubMed
-
- Baker C J. Group B streptococcal infections. Adv Intern Med. 1980;25:475–501. - PubMed
-
- Baker C J. Vaccine prevention of group B streptococcal disease. Pediatr Ann. 1993;22:711–714. - PubMed
-
- Baker C J, Barrett F F. Group B streptococcal infections in infants. The importance of the various serotypes. JAMA. 1974;230:1158–1160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

