Streptococcus sanguis-induced platelet clotting in rabbits and hemodynamic and cardiopulmonary consequences
- PMID: 9826372
- PMCID: PMC108748
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5906-5914.1998
Streptococcus sanguis-induced platelet clotting in rabbits and hemodynamic and cardiopulmonary consequences
Abstract
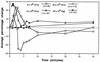
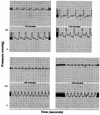
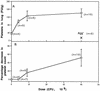
By mimicking hemostatic structural domains of collagen, Streptococcus sanguis (aggregation-positive phenotype; Agg+) induces platelets to aggregate in vitro. To test the hypothesis that aggregation occurs in vivo, S. sanguis (Agg+ or Agg- suspension) was infused intravenously into rabbits. The extent of hemodynamic and cardiopulmonary changes and the fate of circulating platelets were Agg+ strain dose dependent. Within 45 to 50 s of the start of infusion, 40 x 10(8) CFU of the Agg+ strain caused increased blood pressure. Thirty seconds after infusion, other changes occurred. Intermittent electrocardiographic abnormalities (13 of 15 rabbits), ST-segment depression (10 of 15 rabbits), and preventricular contractions (7 of 15 rabbits) manifested at 3 to 7 min, with frequencies dose dependent. Respiratory rate and cardiac contractility increased during this phase. Blood catecholamine concentration, thrombocytopenia, accumulation of 111Indium-labeled platelets in the lungs, and ventricular axis deviation also showed dose dependency. Rabbits were unaffected by inoculation of an Agg- strain. Therefore, Agg+ S. sanguis induced platelet aggregation in vitro. Platelet clots caused hemodynamic changes, acute pulmonary hypertension, and cardiac abnormalities, including ischemia.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dental plaque, platelets, and cardiovascular diseases.Ann Periodontol. 1998 Jul;3(1):151-60. doi: 10.1902/annals.1998.3.1.151. Ann Periodontol. 1998. PMID: 9722699
-
The platelet interactivity phenotype of Streptococcus sanguis influences the course of experimental endocarditis.Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4809-18. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4809-4818.1992. Infect Immun. 1992. PMID: 1398992 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of Streptococcus sanguis on blood composition, blood pressure and cardiac dysfunction in rabbis].Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001 Sep;36(5):354-6. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001. PMID: 11769649 Chinese.
-
Platelet-streptococcal interactions in endocarditis.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1996;7(3):222-36. doi: 10.1177/10454411960070030201. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1996. PMID: 8909879 Review.
-
Platelet activation is a key event in the pathogenesis of streptococcal infections.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015 Jun 1;20(6):910-8. doi: 10.2741/4345. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2015. PMID: 25961531 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of adhesion maintenance by methionine sulphoxide reductase in Streptococcus gordonii.Mol Microbiol. 2011 May;80(3):726-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07603.x. Epub 2011 Mar 16. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21410565 Free PMC article.
-
Ecto-5'-nucleotidase: a candidate virulence factor in Streptococcus sanguinis experimental endocarditis.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038059. Epub 2012 Jun 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22685551 Free PMC article.
-
Type IV Pili of Streptococcus sanguinis Contribute to Pathogenesis in Experimental Infective Endocarditis.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0175221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01752-21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34756087 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Proteasome in Platelet Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 13;22(8):3999. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083999. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activated protein C ameliorates Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin-induced lethal pathogenesis in rats.J Biomed Sci. 2012 Nov 21;19(1):98. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-98. J Biomed Sci. 2012. PMID: 23170801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler D, Nikolic S D, Sonnenbick E H, Yellin E L. Time to dP/dtmax, a preload-independent index of contractility: open-chest dog study. Basic Res Cardiol. 1996;91:94–100. - PubMed
-
- Angrist A A, Oka M, Nakao K. Vegetative endocarditis. Pathol Annu. 1967;2:155–212.
-
- Beck, J., R. Garcia, G. Heiss, P. S. Vokonas, and S. Offenbacher. 1996. Periodontal disease and cardiovascular disease. J. Periodontol. 67(Suppl.; symposium proceedings):1123–1137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

