Characterization of human immunoglobulin (Ig) isotype and IgG subclass response to Bartonella henselae infection
- PMID: 9826373
- PMCID: PMC108749
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.12.5915-5920.1998
Characterization of human immunoglobulin (Ig) isotype and IgG subclass response to Bartonella henselae infection
Abstract
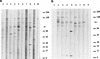
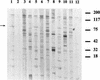
Serologic parameters of cat scratch disease (CSD) were evaluated by Western blot analysis. Sera from patients with serologically confirmed CSD antigen were screened for immunoglobulin (Ig) isotype-specific as well as IgG subclass-specific reactivity against Bartonella henselae whole-cell antigen. Bartonella-negative control sera were used to determine baseline antibody activity. Heterogeneous B. henselae-specific IgG reactivity with numerous protein bands, ranging from >150 to <17 kDa, was observed. Though individual banding patterns were variable, one approximately 83-kDa B. henselae protein (Bh83) was immunoreactive with all CSD sera tested, suggesting it is a conserved antigen during infection. Bh83 was not recognized by reference human antisera against Rickettsia rickettsii, Chlamydia group positive, Treponema pallidum, Orientia tsutsugamushi, Fransciscella tularensis, Ehrlichia chaffeensis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Escherichia coli, although other cross-reactive proteins were evident. Significantly, CSD sera failed to recognize the 83-kDa protein when tested against Bartonella quintana antigen, though sera from B. quintana-infected patients did react to Bh83. This cross-reactivity suggests epitope conservation during infection with B. henselae or B. quintana. Western blot analysis further revealed similar banding patterns when B. henselae was reacted against the Ig isotypes IgG and IgG1 and both secretory and alpha chains of IgA. Neither IgM nor IgE reacted significantly to Bartonella antigen by our Western blot analysis. Dissection of the antibody response at the IgG subclass level indicated that prominent antigen recognition was limited to IgG1. These observations provide insight into induced immunity during CSD and provide evidence for conserved epitope expression during infection with B. henselae or B. quintana.
Figures
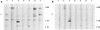
Similar articles
-
Seroprevalence of antibodies to Bartonella henselae in patients with cat scratch disease and in healthy controls: evaluation and comparison of two commercial serological tests.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1998 Jul;5(4):486-90. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.5.4.486-490.1998. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9665953 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative seroreactivity to Bartonella henselae and Bartonella quintana among cats from Israel and North Carolina.Vet Microbiol. 1996 May;50(1-2):95-103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(96)00006-5. Vet Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8810011
-
Utility of Bartonella henselae IgM Western Blot Bands for Serodiagnosis of Cat Scratch Disease.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Dec 26;56(1):e01322-17. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01322-17. Print 2018 Jan. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29093103 Free PMC article.
-
Serological review of Bartonella henselae and Bartonella quintana infection among Malaysian patients with unknown causes of febrile illnesses.Trop Biomed. 2022 Sep 1;39(3):328-331. doi: 10.47665/tb.39.3.004. Trop Biomed. 2022. PMID: 36214431 Review.
-
Bartonella infection in immunocompromised hosts: immunology of vascular infection and vasoproliferation.Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:612809. doi: 10.1155/2012/612809. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22162717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Blood culture-negative endocarditis caused by Bartonella quintana in Iran.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 30;14(1):26063. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77757-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39478136 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an immunoglobulin M capture-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of acute infections with Bartonella henselae.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 Feb;16(2):282-4. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00305-08. Epub 2008 Dec 3. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19052161 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Bartonella henselae-specific immunity in BALB/c mice.Immunology. 1999 Jun;97(2):352-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00750.x. Immunology. 1999. PMID: 10447753 Free PMC article.
-
The Bartonella vinsonii subsp. arupensis immunodominant surface antigen BrpA gene, encoding a 382-kilodalton protein composed of repetitive sequences, is a member of a multigene family conserved among bartonella species.Infect Immun. 2005 May;73(5):3128-36. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.5.3128-3136.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15845521 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Bartonella Quintana Culture-Negative Endocarditis.Am J Case Rep. 2019 Apr 26;20:602-606. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.915215. Am J Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31026253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barka N E, Hadfield T, Patnaik M, Schwartzman W A, Peter J B. EIA for detection of Rochalimaea henselae-reactive IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies in patients with suspected cat-scratch disease. J Infect Dis. 1993;167:1503–1504. - PubMed
-
- Dalton M J, Robinson L E, Cooper J, Regnery R L, Olson J G, Childs J E. Use of Bartonella antigens for serologic diagnosis of cat-scratch disease at a national referral center. Arch Intern Med. 1995;155:1670–1676. - PubMed
-
- Dolan M J, Wong M T, Regnery R L. Syndrome of Rochalimaea henselae adenitis suggesting cat scratch disease. Ann Intern Med. 1993;118:331–336. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

